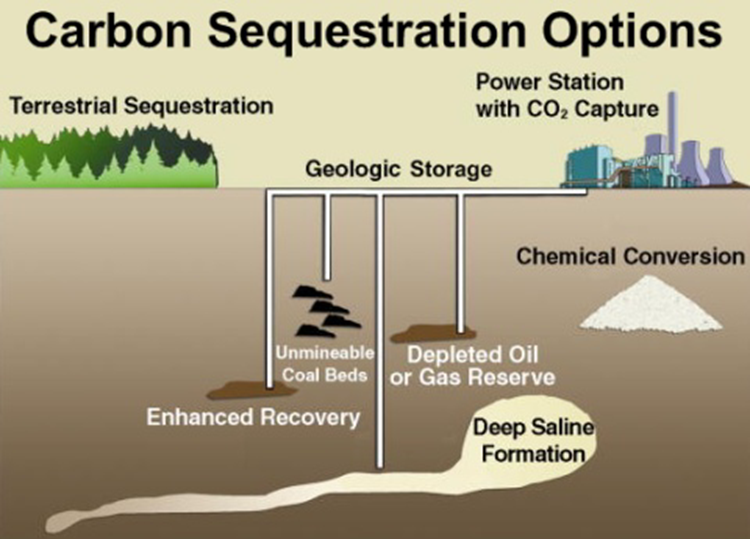
About:- Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) for long-term removal. This occurs through both natural processes and artificial technological interventions.
1. Natural Sequestration:
Natural processes by which ecosystems capture and hold carbon:
- Terrestrial: Plants absorb CO2 via photosynthesis, storing carbon in biomass (trunks, roots, foliage) and soils.
- Oceanic: Oceans serve as a major carbon sink, naturally absorbing, releasing, and storing large quantities of CO2 from the atmosphere.
2. Artificial Sequestration
Technological methods used to capture CO2, typically at an emission source, and store it:
- Geological: CO2 is captured from sources (e.g., industrial facilities) and injected into deep underground formations. Storage sites include depleted oil and gas reservoirs, unmineable coal seams, and deep saline aquifers.
- Oceanic: Involves engineered methods, such as:
- Direct Injection: Pumping captured CO2 directly into the deep ocean.
- Iron Fertilization: Adding iron to stimulate phytoplankton blooms, which absorb CO2 through photosynthesis.