Context :- The Supreme Court has expressed concern over the delay in implementing the Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam (106th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2023),
The 106th Constitutional Amendment Act, :-
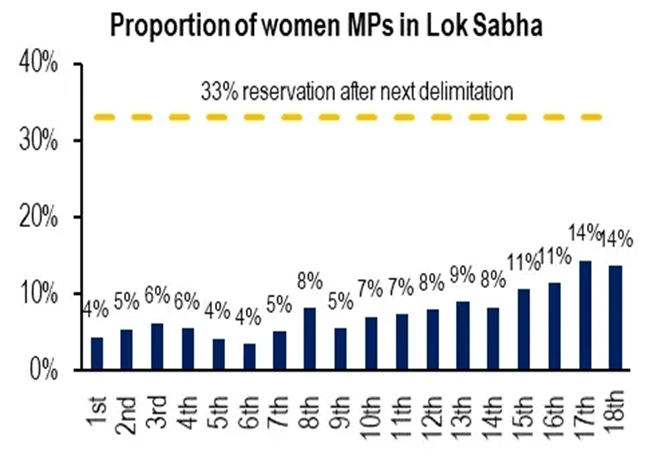
The 106th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2023, officially titled the Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam, mandates a one-third (33%) reservation for women in the Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and the Legislative Assembly of Delhi.
Key Constitutional Provisions :
- Article 330A: Mandates one-third reservation for women in the Lok Sabha, including sub-reservation within SC/ST seats.
- Article 332A: Mandates one-third reservation for women in State Legislative Assemblies, including sub-reservation within SC/ST seats.
- Article 239AA: Extends the one-third reservation to the Delhi Legislative Assembly.
- Article 334A: This article governs the implementation and duration of the reservation.
- The 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments (1992), :- Based on the National Perspective Plan for Women (1988–2000), mandated one-third reservation for women in Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) and urban local bodies.
- .Article 243D :- guarantees at least one-third reservation for women in both directly elected seats and offices of chairpersons in PRIs.
- Implementation: Begins only after the census and delimitation exercise following the Act’s commencement.
- Duration: Establishes a 15-year sunset clause (renewable by Parliament).
- Rotation:Reserved seats will be rotated after each delimitation.
State initiatives:-
- Bihar became the first State (2006) to introduce 50% reservation for women in panchayat bodies.
- Over 20 States now provide 50% reservation for women at the panchayat level.
In panchayats and municipalities, there exists:
1. Vertical reservation for SCs, STs, and OBCs
2. Horizontal reservation for women across all categories — General, SC, ST, and OBC.
Types of Reservation in the Indian Constitutional Framework :-
- Vertical Reservation:
- Refers to reservation for SCs, STs, and OBCs, applied separately to each group as defined by law.
- Envisioned under Article 16(4) of the Constitution.
- Horizontal Reservation:
- Ensures equal opportunity for groups such as women, veterans, persons with disabilities, and the transgender community, cutting across all vertical categories.
- Envisaged under Article 15(3) of the Constitution.
Major Concerns and Analysis:-
- Contingent Implementation: The Act’s rollout is delayed indefinitely, as it is contingent upon the completion of the next census and subsequent delimitation.
- Limited Scope: The reservation applies only to directly elected Lower Houses (Lok Sabha, Assemblies) and excludes Upper Houses (Rajya Sabha, Legislative Councils).
- Risk of Proxy Representation: There is a significant concern of “tokenism” or the “Sarpanch Pati” phenomenon, where male relatives wield de facto power.
- Impact of Rotation: The mandatory rotation of reserved seats might disincentivize long-term constituency development by elected representatives.