Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is an investment made by an entity (company or individual) from one country into a business located in another country. It is characterized by the intent to establish a lasting interest and exert significant management control over the foreign enterprise.
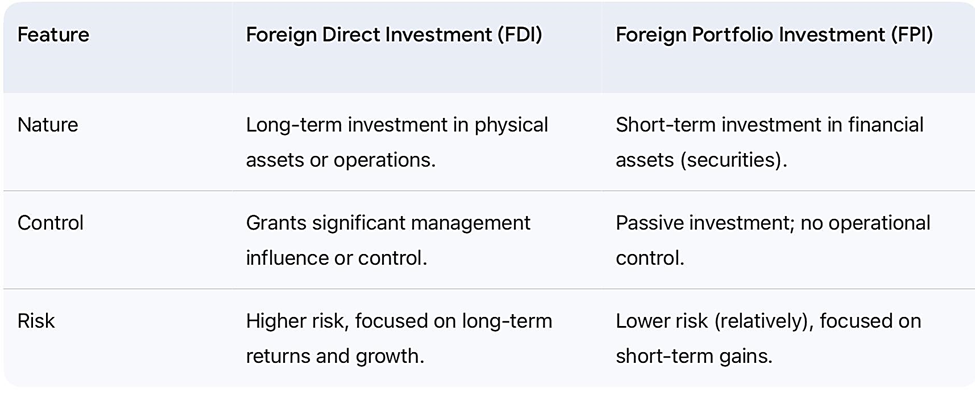
This is distinct from Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI), which involves acquiring financial assets like stocks and bonds.
Methods and Types of FDI
FDI can be categorized based on the method of entry and the nature of the operation.
1. Methods of Investment:
- Greenfield Investment: Involves establishing a completely new operation (e.g., building a new factory or office) from the ground up in the host country. This allows for maximum control over the new venture.
- Brownfield Investment: Occurs when a foreign entity acquires or merges with an existing company in the host country, utilizing its established infrastructure and market presence.
2. Types of Operations:
- Horizontal FDI: The investor establishes the same type of business operation in the foreign country as it runs in its home country (e.g., a car manufacturer opening a new plant abroad).
- Vertical FDI: The investment is made in a complementary business, often part of the investor’s supply chain (e.g., a car manufacturer investing in a foreign tyre company).
- Conglomerate FDI: The investor acquires or establishes a business in a foreign country that is unrelated to its core operations (e.g., a tech firm investing in a fashion brand).
How Does India Regulate FDI?
India facilitates FDI through two primary channels, balancing openness with national security and economic priorities.
- Automatic Route: FDI is permitted in most sectors without prior approval from the government or the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), subject to specific sectoral conditions.
- Government Route: Entry requires explicit prior approval from the concerned government ministry or department. This route is mandated for sensitive sectors or when investment limits are breached.
Where is India’s FDI Coming From? (FY 2023-24 Trends)
Understanding the sources and destinations of FDI is critical for analyzing economic health and foreign relations.
Top 5 FDI Sources (FY 2023-24):
1. Mauritius (25%)
2. Singapore (23%)
3. USA (9%)
4. Netherland (7%)
5. Japan (6%)
Top 5 Sectors Receiving FDI (FY 2023-24):
1. Services Sector (Finance, Banking, etc.): 16%
2. Computer Software & Hardware: 15%
3. Trading: 6%
4. Telecommunications: 6%
5. Automobile Industry: 5%