The Great Nicobar Project:
- Project: A Rs 72,000-crore comprehensive infrastructure development on Great Nicobar Island,
- Implementing Agency: Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
Geographic & Ecological Context
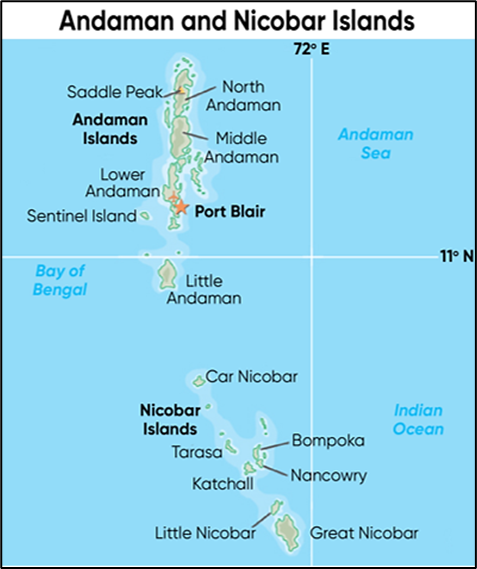
- Location: Great Nicobar Island (Area: 910 sq km), which contains Indira Point, India’s southernmost tip.
- Strategic Position: Located near the Malacca Strait, a critical global shipping chokepoint.
- Topography: Hilly and covered with lush tropical rainforests (high rainfall: ~3,500 mm).
- Coastal Flora: Includes Mangroves and Pandan forests.
Legal Conflict & Key Risks:
- Core Legal Dispute: Diversion of forest land allegedly violating the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006.
- Administration’s Stance: Argued that the Protection of Aboriginal Tribes Regulation (PATR), 1956, already protects tribal rights, making FRA implementation unnecessary.
- Key Legal Difference: The FRA (2006) mandates prior consent from the Gram Sabha after vesting rights. The PATR (1956) allows the administration unilateral authority.
- Affected Tribes:
- Shompen (a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group – PVTG).
- Nicobarese.
- Geological Risk: The island is in a highly seismic zone (Zone V), near the fault line of the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami.