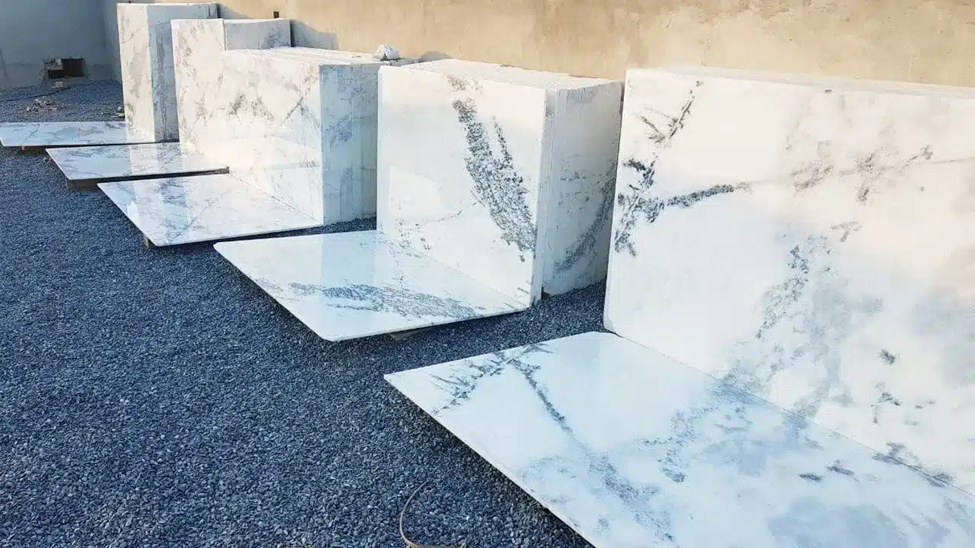
Context :- The Geographical Indications Registry, Ministry of Commerce & Industry, has granted the GI tag to Ambaji Marble from Banaskantha district, Gujarat.
- Definition: A GI is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation attributable to that origin.
- Applicability: GIs are typically used for agricultural, natural, or manufactured goods, as well as handicrafts, industrial products, and foodstuffs.
- Protection: GI registration provides legal protection to producers, preventing unauthorized parties from using the product’s name.
Current Status in India
- First GI Tag: Darjeeling Tea (2004-2005).
- Total GI Tags: 658 products registered as of August 2025.
- Leading States: Uttar Pradesh holds the highest number of GI-tagged products, followed by Tamil Nadu.
International Framework
- TRIPS Agreement:GIs are formally recognized as IPRs under the WTO’s Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights.
- Paris Convention (1883): Provides the foundational multilateral framework for the protection of industrial property, including GIs.
- Lisbon Agreement (1958): Establishes an international registration system specifically for appellations of origin (a type of GI).
- Madrid System: While focused on trademarks, it can be utilized to protect GIs registered as collective or certification marks internationally.
Governance Framework in India:
- Governing Legislation: The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration andProtection) Act, 1999.
- Administrative Body: The Geographical Indications Registry, operating under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DIPIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
GI Act, 1999
- Establishes the Geographical Indications Registry to process applications.
- Defines registration criteria based on the product-origin link and associated quality.
- Sets protection at 10 years, with indefinite renewal.
- Outlines civil and criminal penalties for infringement.
- Manages the registration of authorized users and producer associations.
About Ambaji White Marble
- Definition: A marble distinguished by its white appearance and unique natural patterns, named after its primary quarrying location in Ambaji, Gujarat.
- Alternate Names: Amba White Marble, Ambe White Marble.
- Characteristics: Features a pristine white base with varied, subtle grey or beige veining (ranging from fine to bold). It is known for its high durability, lasting shine, and smooth, polished surface.
- Application: Widely utilized in luxury architectural projects, monuments, and sculptures.
Key Facts: Marble
- Geological Type: A metamorphic rock.
- Formation: Results from the metamorphism (subjecting to heat and pressure) of limestone or dolostone.
- Composition: Composed primarily of interlocking calcite crystals (CaCO3), often with secondary minerals like micas, quartz, or iron oxides.
Formation Processes:
- Regional Metamorphism: Occurs on a large scale at convergent plate boundaries.
- Contact Metamorphism: Occurs when a hot magma body heats adjacent limestone or dolostone.