About :- A Payments Bank is a specialized, non-universal banking entity operating on a smaller scale without undertaking credit risk. It was established based on the recommendations of the Nachiket Mor Committee to advance financial inclusion.
Objective:
To provide basic banking services to unbanked and underbanked populations, including low-income households, migrant laborers, and small entrepreneurs.
Legal Framework:
Payments Banks are registered as public limited companies (Companies Act, 2013) and licensed under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949. They are governed by various statutes, including the RBI Act, 1934, and the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
Key Requirements:
- Capital: Minimum paid-up equity capital is Rs. 100 crores.
- Promoter Stake: Promoters must maintain a minimum 40% stake for the first five years.
Permitted Activities:
- Deposits: Acceptance of demand deposits (savings and current accounts) up to a limit of Rs. 2,00,000 per customer.
- Investments: Must invest 75% of demand deposit balances in Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR)-eligible government securities. The remaining 25% must be placed as deposits with other scheduled commercial banks.
- Services: Offer remittance services, mobile payments, ATM/debit cards, and net banking.
- Correspondent Banking: May act as a Banking Correspondent (BC) for other banks.
Prohibited Activities:
- Cannot issue loans or credit cards.
- Cannot accept time deposits (e.g., Fixed Deposits) or NRI deposits.
- Cannot set up non-banking financial (NBFC) subsidiaries.
Small Finance Banks
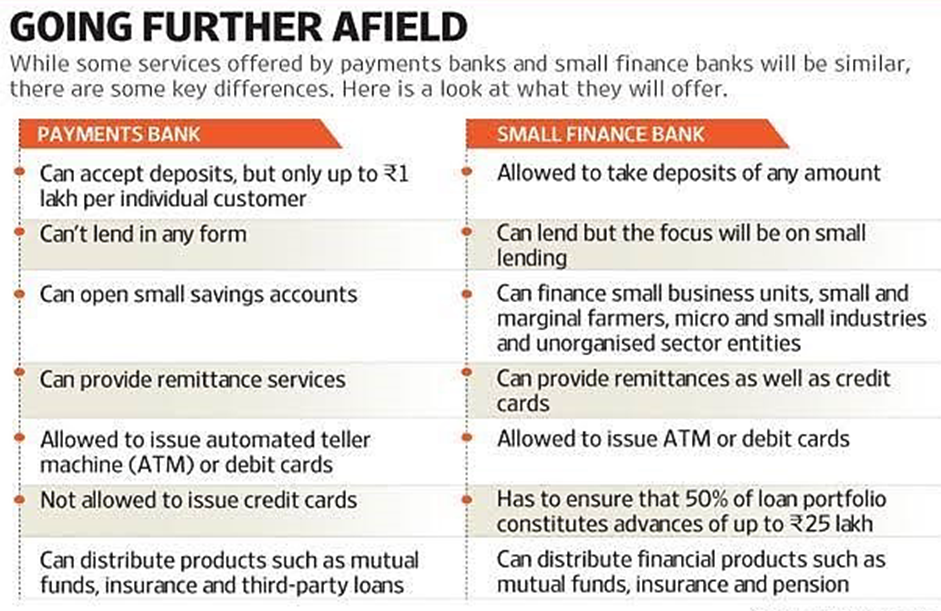
Small Finance Banks (SFBs) are RBI-regulated scheduled commercial banks established as public limited companies to provide financial inclusion to small businesses, micro-industries, and unorganized sectors.
They must adhere to all prudential norms of commercial banks, including CRR and SLR.
Key operational mandates include:
- Capital: Minimum paid-up equity of ₹200 crore (₹100 crore for converted UCBs).
- Priority Sector Lending (PSL): 75% of credit must be allocated to PSL.
- Rural Branches: 25% of branches must be in unbanked rural areas.
- Loan Size: 50% of the loan portfolio must be under ₹25 lakhs.
SFBs offer full banking services, including lending, and may also distribute non-risk products (e.g., mutual funds, insurance) and conduct foreign exchange business. Existing NBFCs, MFIs, and LABs are eligible for conversion into SFBs.