With major powers like the US and China accelerating their timelines for establishing long-term lunar settlements, researchers are actively developing Lunarcrete as a viable construction material to withstand the Moon’s harsh environment.
1. What is Lunarcrete?
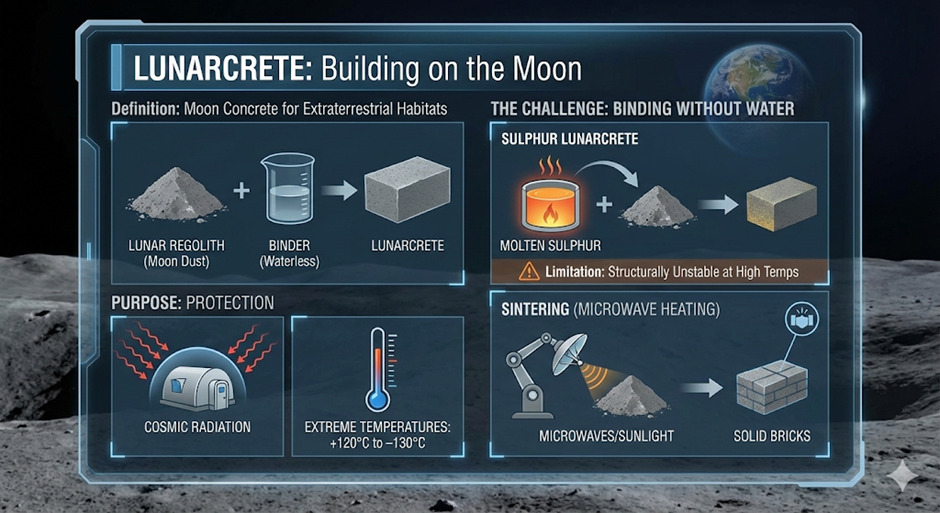
- Definition: An umbrella term for “Moon Concrete,” a hypothetical construction material designed for extraterrestrial habitats.
- Composition: Unlike terrestrial concrete (which uses sand and gravel), Lunarcrete utilizes Lunar Regolith (loose moon soil/dust) as the primary aggregate.
- Purpose: To build habitats capable of protecting astronauts from:
- Cosmic Radiation: The Moon lacks a protective atmosphere/magnetosphere.
- Extreme Temperatures: Swings ranging from 120°C to –130°C.
2. The Challenge: Binding without Water
Standard concrete relies on Portland cement and water. Since water is a scarce and precious resource on the Moon, scientists are developing waterless binding techniques:
- Sulphur Lunarcrete:
- Process: Mixing lunar regolith with molten sulphur.
- Mechanism: Sulphur acts as the binding agent upon cooling and solidifying.
- Limitation: While water-free, it has a low melting point, making it structurally unstable in high-temperature lunar days.
- Sintering (Microwave Heating):
- Process: Using concentrated sunlight or microwaves to heat regolith.
- Mechanism: The heat causes the soil grains to melt and fuse (sinter) into solid bricks, eliminating the need for any external binder.
3. Thermal Properties & Viability
A recent simulation by Louisiana State University (LSU) highlighted the material’s insulation capabilities:
- Temperature Regulation: A Lunarcrete dome successfully maintained an internal temperature of 22°C despite external fluctuations between 120°C and –130°C.
- Structural Design: Walls constructed with two layers of Lunarcrete separated by a vacuum (empty space) provided the most effective thermal insulation.
Q. Lunarcrete, which was recently in the news, refers to which of the following?
A. A method of extracting oxygen and hydrogen from lunar ice deposits.
B. A building material using lunar regolith as aggregate and sulphur or heat fusion as a binder.
C. A specialized fabric designed to protect astronauts from lunar dust and radiation.
D. A water-intensive cement mixture imported from Earth for lunar construction.
SOL. B
Lunarcrete (often called Moon Concrete) is a hypothetical construction material designed for building habitats on the Moon. It distinguishes itself from terrestrial concrete by using Lunar Regolith (Moon soil/dust) as the primary aggregate instead of sand or gravel.
To address the scarcity of water on the Moon, it utilizes alternative binding methods such as Sulphur (which melts and re-solidifies) or Sintering (using microwaves/sunlight to fuse soil grains), rather than water-intensive Portland cement. Therefore, option B is the correct answer.