The Union government has introduced the [The Viksit Bharat–Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin)} VB-G RAM G Bill ]to repeal and replace the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), 2005, aligning the framework with the vision of Viksit Bharat @2047.
1.What is the Fundamental Structural Shift?
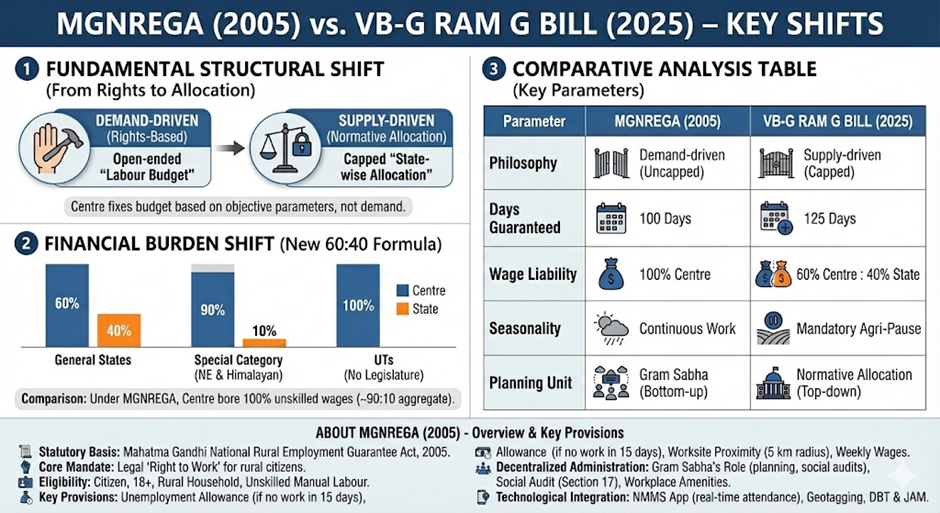
The framework transitions from a “Demand-Driven” (Rights-based) model to a “Supply-Driven” (Normative Allocation) model.
Unlike the open-ended “Labour Budget” of MGNREGA, the Centre will now fix a “State-wise Normative Allocation” based on objective parameters.
2. How does the Financial Burden Shift?
- The 60:40 Formula (Section 22): The Bill drastically alters the funding pattern, increasing the fiscal liability of States.
- General States: 60:40 (Centre : State).
- Special Category (NE & Himalayan States): 90:10 (Centre : State).
- UTs (No Legislature): 100% Centre.
Comparison : Under MGNREGA, the Centre bore 100% of unskilled wages, effectively resulting in a ~90:10 aggregate split.
| Parameter | MGNREGA (2005) | VB-G RAM G Bill (2025) |
| Philosophy | Demand-driven (Uncapped) | Supply-driven (Capped) |
| Days Guaranteed | 100 Days | 125 Days |
| Wage Liability | 100% Centre | 60% Centre : 40% State |
| Seasonality | Continuous Work | Mandatory Agri-Pause |
| Planning Unit | Gram Sabha (Bottom-up) | Normative Allocation (Top-down) |
3. About MGNREGA?
Overview & Genesis
- Statutory Basis: Enacted as the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005.
- Core Mandate: Legally guarantees the “Right to Work” to rural citizens.
Eligibility Criteria
- Must be a Citizen of India.
- Age: 18 years or above.
- Residence: Must belong to a Rural Household.
- Nature of Work: Willingness to perform unskilled manual labour.
Key Statutory Provisions
- Unemployment Allowance: If work is not provided within 15 days of application, the applicant is entitled to an allowance (1/4th of wage for first 30 days; 1/2 thereafter).
- Worksite Proximity: Employment is typically provided within a 5 km radius; travel allowance is mandatory if the distance exceeds this limit.
- Wages: Paid weekly (mandatorily within 15 days) directly to bank accounts.
Decentralized Administration
- Gram Sabha’s Role: The principal authority for planning and social audits; must recommend at least 50% of the works.
- Social Audit (Section 17): Mandated to ensure transparency, community participation, and accountability in execution.
- Workplace Amenities: Implementing agencies must ensure crèche facilities, drinking water, and first-aid at worksites.
Technological Integration
- NMMS App: The National Mobile Monitoring Software was made mandatory (Jan 2023) for capturing real-time, geotagged attendance twice a day.
- Geotagging: Mandatory geotagging of assets to prevent duplication and fraud.
- DBT & JAM: Integration with Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile for transparent wage transfers.
Q. With respect to the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), 2005, consider the following statements:
1.If the government fails to provide employment within 15 days of receipt of the application, the applicant is entitled to a daily unemployment allowance.
2. Section 17 of the Act mandates the Social Audit of all works executed under the scheme.
3. The National Mobile Monitoring Software (NMMS) App is mandatory for capturing real-time attendance at worksites.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Answer: C
Solution:
Statement 1 is Correct: Under Section 7 of the MGNREGA, 2005, if an applicant for employment is not provided such employment within 15 days of receipt of the application, they are entitled to a daily unemployment allowance.
Statement 2 is Correct: Section 17 of the Act legally mandates the conduct of a Social Audit of all works executed under the scheme. This audit is primarily conducted by the Gram Sabha to ensure transparency and accountability.
Statement 3 is Correct: The government has made the use of the National Mobile Monitoring Software (NMMS) App mandatory (effective from January 1, 2023) for capturing real-time, geotagged attendance of workers at worksites to check corruption and improve monitoring.