Why in the News?
- Iran has recently entered a state of high military readiness following threats of preemptive strikes issued by its Army Chief, Major General Amir Hatami.
- This stance is a direct response to escalating external rhetoric from the United States, specifically regarding potential American intervention in Iran’s internal civil unrest.
- Domestically, Iran is grappling with economic instability and protests, while externally, it seeks to maintain its regional dominance against the perceived dual threat of the U.S.-Israel alliance.
Political and Administrative Profile of Iran
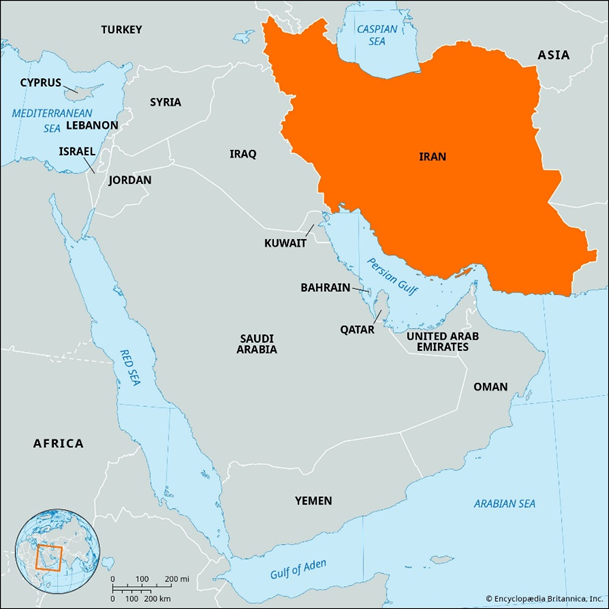
- Iran is a strategically located West Asian country situated at the junction of Central Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East.
- Capital: Tehran.
- International Groupings: Iran is a member of OPEC, BRICS, and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), reflecting its growing engagement with non-Western multilateral platforms.
- Iran’s geographical position provides:
- Strategic depth through extensive land boundaries with seven countries.
- Maritime access to critical international sea lanes through the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman.
- Proximity to conflict-prone regions such as Mesopotamia, the Caucasus, and the Arabian Peninsula.
- It controls access near the Strait of Hormuz, a vital maritime chokepoint between Iran and Oman that connects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman-through which a significant share of global crude oil trade passes.
International Boundaries and Neighbours of Iran
- Land Boundaries: Iran shares land borders with seven countries, making it one of the most geopolitically connected states in West Asia.
- Northern borders include Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan, linking Iran to the Caucasus and Central Asia.
- Eastern borders with Afghanistan and Pakistan place Iran close to South Asian and security-sensitive regions.
- Western borders with Iraq and Turkey connect Iran directly to Arab West Asia and Europe-linked Anatolia.
- Maritime Boundaries:
- North: The Caspian Sea lies to the north and represents an important zone for energy resources and regional diplomacy.
- South: The Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman lie to the south, giving Iran access to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
Iran and the Persian Gulf
- Location: The Persian Gulf lies to the south of Iran and forms Iran’s primary south-western maritime boundary.
- Iranian Coastline: Iran’s coast along the Persian Gulf runs parallel to the Zagros Mountain foothills, with narrow coastal plains rising inland.
- Northern Boundary: The entire northern coastline of the Persian Gulf is formed by Iran, giving it continuous control over the northern littoral.
- Southern Boundary: The southern coast is shared by Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates, all part of the Arabian Peninsula.
- Western End: The gulf narrows near Kuwait and southern Iraq, where the Shatt al-Arab river system drains into it.
- Eastern Connection: The Persian Gulf connects to the Gulf of Oman through the Strait of Hormuz, a critical maritime chokepoint.
Iran and the Gulf of Oman
- Location: The Gulf of Oman lies to the south-east of Iran and provides direct access to the Arabian Sea.
- Iranian Coastline: Iran’s coastline along the Gulf of Oman is known as the Makran Coast, which is strategically significant.
- Northern Boundary: The northern boundary of the Gulf of Oman is formed by Iran’s Makran coast.
- Southern Boundary: The southern boundary is formed by Oman and parts of the United Arab Emirates.
- Western Entrance: The Strait of Hormuz marks the western entrance of the Gulf of Oman and separates it from the Persian Gulf.
- Eastern Opening: The Gulf of Oman opens eastward into the Arabian Sea, forming part of the Indian Ocean system.
Physical Geography of Iran
- Relief and Land Surface: Iran’s landscape is largely shaped by the Iranian Plateau, which includes expansive arid zones and deserts, notably the Dasht-e Kavir and the Dasht-e Lut.
- Major Mountain Systems: The country is bordered by prominent mountain ranges, with the Zagros Mountains (long folded range) stretching across western Iran and the Alborz Mountains extending along the northern margins near the Caspian Sea.
- Highest Elevation Point: Mount Damavand, a prominent stratovolcanic peak, located within the Alborz Mountain system, represents the highest point in Iran.
- Climatic Conditions: Iran displays considerable climatic variation, ranging from dry and semi-dry climates over the interior plateau to humid subtropical conditions along the Caspian coastal belt.
- River Systems: Rivers such as the Karun, Dez, Karkheh, and Diyala are vital for agricultural irrigation and water supply, especially in the western and south-western regions.
- Lake Urmia: It is an endorheic salt lake in northwestern Iran between the Azerbaijan provinces, historically the largest lake in the Middle East and among the largest saltwater lakes globally.
- Mineral and Energy Wealth: Iran possesses extensive hydrocarbon reserves, particularly oil and natural gas, along with notable deposits of coal, chromium, copper, iron ore, lead, manganese, zinc, and sulphur.
Q. Which of the following countries share a land boundary with Iran?
1. Armenia
2. Azerbaijan
3. Afghanistan
4. Kazakhstan
Select the correct answer using the code below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2 and 3 only
Explanation
Armenia — Correct: Armenia shares a direct land boundary with north-western Iran. Although the border is short, it is strategically important as it links Iran with the Caucasus region.
Azerbaijan — Correct: Iran shares land borders with Azerbaijan, both with the main Azerbaijani territory and the Nakhchivan exclave, making Azerbaijan a confirmed land neighbour of Iran.
Afghanistan — Correct: Afghanistan shares a long eastern land boundary with Iran, which is significant for security, trade, and migration considerations.
Kazakhstan — Incorrect: Kazakhstan does not share a land boundary with Iran. The two countries are separated by the Caspian Sea, and therefore do not have a direct terrestrial border.