Context
Recently, on February 9, 2026, the Union Defence Minister of India, Rajnath Singh, held a high-level bilateral meeting with the Greek Minister of National Defence, Nikos Dendias, at the Manekshaw Centre in New Delhi.
1. Evolution of Strategic Ties
- 1998 MoU: Bilateral defense cooperation is rooted in a Memorandum of Understanding signed in 1998, which was notably established despite international sanctions against India following the Pokhran-II nuclear tests.
- Strategic Partnership (2023): During PM Narendra Modi’s visit to Athens in August 2023, the relationship was elevated to a Strategic Partnership, prioritizing security and defense.
- Gateway to Europe: Greece is increasingly viewed as India’s primary strategic anchor in the Mediterranean and a gateway for the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
2. Joint Military Exercises and Interoperability
- Air Force Cooperation:
- Exercise INIOCHOS: The Indian Air Force (IAF) has become a regular participant in this multinational exercise hosted by the Hellenic Air Force at Andravida Air Base.
- Exercise Tarang Shakti (2024): Greece participated in India’s largest multinational air exercise with F-16 fighter jets, marking a significant upgrade in tactical synergy.
- Naval Cooperation:
- Maiden Maritime Exercise (2025): The Indian Navy (represented by INS Trikand) and the Hellenic Navy conducted their first bilateral exercise in the Mediterranean Sea near Salamis Naval Base.
- Port Calls: Regular visits of Indian warships to the Souda Bay in Crete, a vital NATO naval base, underscore the depth of maritime logistics cooperation.
- Army Cooperation:
- Joint Services Staff Talks: Institutionalized in early 2026 to coordinate long-term military-to-military engagement and training programs.
3. Defense-Industrial and Technology Collaboration
- Joint Ventures: Both nations are exploring collaboration in drone technology, cybersecurity, and shipbuilding.
- Maintenance and Repair: Discussions are underway for India to provide maintenance support for Greece’s fleet, potentially leveraging the commonality in certain aerospace platforms.
- Innovation: The MCP-2026 emphasizes cooperation in “Special Operations” and defense innovation hubs.
4. Strategic and Multilateral Alignment
- Maritime Security: Both nations advocate for a “Free and Open Indo-Pacific” and a rule-based order in the Mediterranean, adhering strictly to the UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea).
- Mutual Interests: Greece consistently supports India on the Kashmir issue and its bid for a permanent seat in the UNSC, while India supports Greece on the Cyprus issue.
- Counter-Terrorism: Cooperation through intelligence sharing, specifically targeting transnational terror networks in the Mediterranean region.
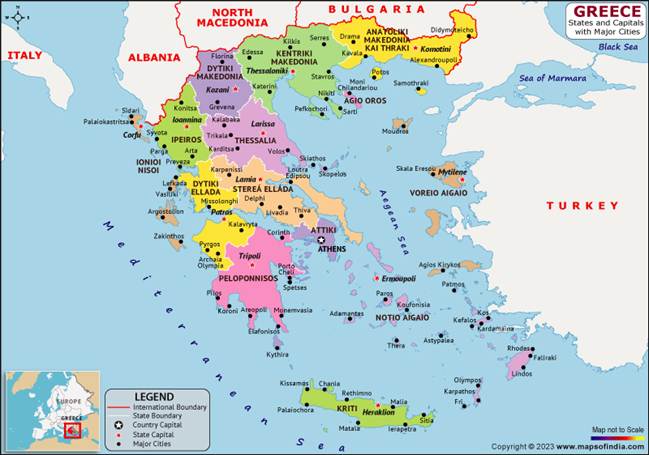
5. Greece – Key Map Points
| Located in Southeastern Europe at the junction of Europe–Asia–Africa.Surrounded by three seas:Aegean Sea (east)Ionian Sea (west)Mediterranean Sea (south)Borders:North – Albania, North Macedonia, BulgariaEast – TurkeyImportant Straits:Dardanelles (connects Aegean Sea to Sea of Marmara)Bosporus (connects Sea of Marmara to Black Sea) (Together called the Turkish Straits – strategically vital)Key Islands:Crete – largest island (southernmost)Rhodes – near TurkeyCyclades & Dodecanese groups (Aegean Sea)Peninsulas:Peloponnese – separated by Corinth CanalStrategic importance:Gateway between Black Sea & Mediterranean trade routesNATO & EU member |
Q. With reference to the defense relations between India and Greece, consider the following statements:
1. The first-ever bilateral maritime exercise between the Indian Navy and the Hellenic Navy was conducted in the Mediterranean Sea in 2025.
2. Greece is a signatory to the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and supports India’s permanent membership in the UN Security Council.
3. ‘Exercise INIOCHOS’ is a bilateral army exercise conducted annually between the Indian and Greek special forces.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
Correct Answer: A
Explanation
• STATEMENT 1 CORRECT: In September 2025, the Indian Navy (INS Trikand) and the Hellenic Navy successfully conducted their maiden bilateral naval exercise in the Mediterranean Sea.
• STATEMENT 2 CORRECT: Greece has ratified the ISA framework and consistently backs India’s core foreign policy objectives, including UNSC reforms and the Kashmir issue.
• STATEMENT 3 INCORRECT: ‘Exercise INIOCHOS’ is a multinational air force exercise hosted by Greece, not a bilateral army exercise. India participated in it with Su-30 MKI aircraft to enhance aerial combat interoperability.