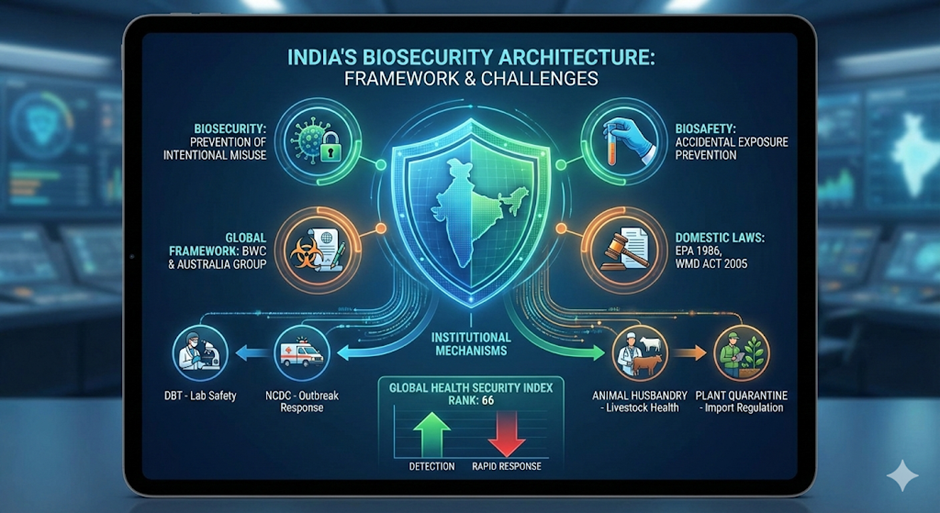
With rising bio-risks (zoonosis, bioterrorism), India is pivoting towards a unified National Biosecurity Framework to integrate its currently fragmented response mechanisms.
Biosecurity vs. Biosafety
- Biosecurity: Focuses on prevention of intentional misuse (e.g., bioterrorism, theft of pathogens). It protects human, animal, and plant health.
- Biosafety: Focuses on prevention of accidental exposure (e.g., lab leaks, unintentional release).
- Relationship: Robust biosafety is a prerequisite for effective biosecurity.
2. Global Framework: Biological Weapons Convention (BWC)
- Year: Came into force in 1975.
- Significance: First multilateral disarmament treaty banning the production of an entire category of weapons.
- Mandate: Prohibits development, production, and stockpiling of biological agents for hostile purposes.
- Unique Feature: It mandates the destruction of existing stockpiles.
- India’s Stance: India is a signatory to the BWC
- 3. India’s Domestic Legal Framework
- Environment (Protection) Act, 1986:
- Governing Law for hazardous microorganisms and Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs).
- Rules: The Biosafety Rules, 1989 were framed under this Act.
- WMD Act, 2005:
- Full Name: Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Act, 2005.
- Function: Criminalizes the manufacture, transport, or transfer of biological weapons.
- Disaster Management Act, 2005:
- NDMA has issued specific guidelines for the Management of Biological Disasters.
Q. With respect to the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC), consider the following statements:
1. It is the first international treaty to ban the entire category of biological weapons of mass destruction.
2. It mandates the destruction of existing stockpiles of biological weapons by the signatory nations.
3. India is a signatory to the Biological Weapons Convention.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is Correct: The Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) is the first multilateral disarmament treaty to ban an entire category of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD). It opened for signature in 1972 and entered into force in 1975.
Statement 2 is Correct: The full title of the treaty is "The Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on their Destruction." Under Article II of the Convention, each State Party undertakes to destroy, or to divert to peaceful purposes, all agents, toxins, weapons, equipment, and means of delivery as soon as possible (no later than nine months after entry into force).
Statement 3 is Correct: India is a key signatory and party to the convention. India signed and ratified the BWC in 1974 and has been a strong proponent of its implementation.