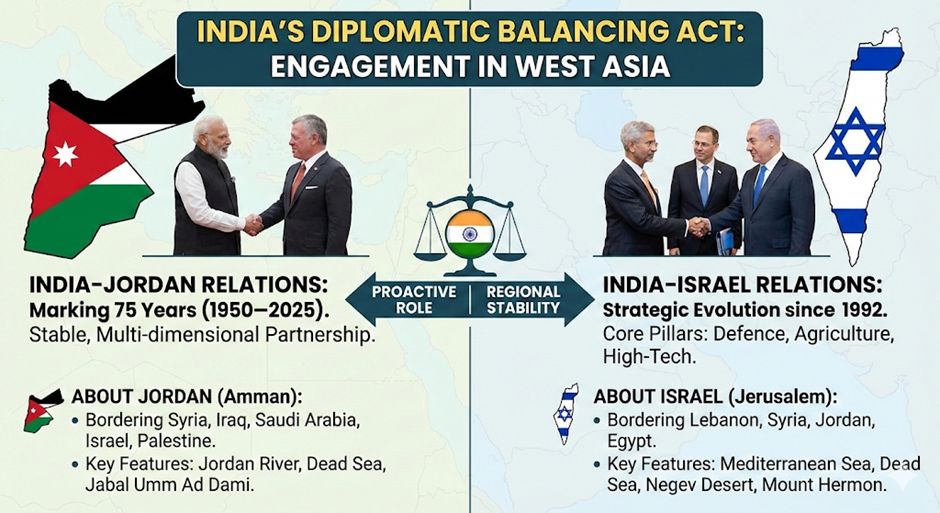
India recently executed a significant diplomatic engagement in West Asia with Prime Minister Narendra Modi visiting Jordan and External Affairs Minister (EAM) S. Jaishankar visiting Israel simultaneously. The visits highlight India’s balancing act and willingness to play a proactive role in regional stability.
India Jordan Relations :
India and the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan are marking 75 years of diplomatic relations (1950–2025), underscoring a mature, stable, and multi-dimensional bilateral partnership. Rooted in mutual trust, political convergence, and shared regional concerns, India–Jordan relations have progressively expanded across political, strategic, economic, developmental, and people-to-people domains.
ABOUT JORDAN
Jordan (Capital: Amman)
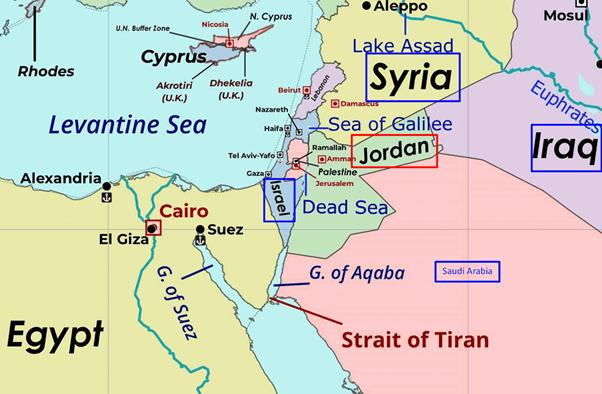
- Geopolitical Location: Situated in West Asia, occupying the northern region of the Arabian Peninsula.
- Bordering Nations:
- North: Syria
- Northeast: Iraq
- South and East: Saudi Arabia
- West: Israel and Palestine (West Bank)
- Maritime Boundaries & Water Bodies: bounded by the Jordan River and the Dead Sea to the west, with access to the Red Sea via the Gulf of Aqaba in the southwest.
- Key Geographical Features:
- Highest Point: Jabal Umm Ad Dami (approx. 1,854 meters).
- Major Rivers: The Jordan River (forming the western border) and the Yarmouk River (major tributary).
India-Israel Relations:
- Diplomatic Timeline: India recognized Israel in 1950, but full diplomatic ties were established only in 1992.
- Geopolitical Context: Early relations were constrained by India’s NAM policy and Arab support, contrasting with Israel’s Western alignment.
- Core Pillars: Since 1992, cooperation has been anchored primarily in defence and agriculture.
- Future Trajectory: The partnership is now pivoting towards high-tech collaboration and innovation.
ABOUT ISRAEL :
Israel (Capital: Jerusalem)
- Location: Located in the Southern Levant region of West Asia, on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea.
- Bordering Nations:
- North: Lebanon
- Northeast: Syria
- East: Jordan and the West Bank
- Southwest: Egypt and the Gaza Strip
- Bordering Water Bodies: Mediterranean Sea (West), Red Sea (South – via Gulf of Aqaba), Dead Sea (East), Sea of Galilee (Northeast).
- Geographical Features:
- Highest Point: Mount Hermon (in the Golan Heights).
- Lowest Point: The Dead Sea (Earth’s lowest elevation on land).
- Key Rivers: Jordan River, Yarkon River, Kishon River.
- Deserts: The Negev Desert covers the southern half of the country.
- Cultural Heritage: Includes UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as Masada, the Old City of Acre, and the White City of Tel Aviv.
Important Geographical Locations of Israel
- Golan Heights: A strategic rocky plateau in the north, bordering Syria.
- West Bank: A landlocked territory near the Mediterranean coast, bordered by Jordan to the east and the Green Line to the south, west, and north.
- Gaza Strip: A small Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, bordering Egypt on the southwest.
- Sea of Galilee (Lake Tiberias): The lowest freshwater lake on Earth and a major water source.
- Negev Desert: A large desert region in southern Israel, home to the Ramon Crater (Makhtesh Ramon).
Q. With reference to the geography of West Asia, consider the following countries:
1. Lebanon
2. Syria
3. Iraq
4. Egypt
Which of the countries given above share a land border with Jordan?
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north and Iraq to the northeast. It does not share a land border with Lebanon (separated by Syria and Israel) or Egypt (separated by the Gulf of Aqaba).