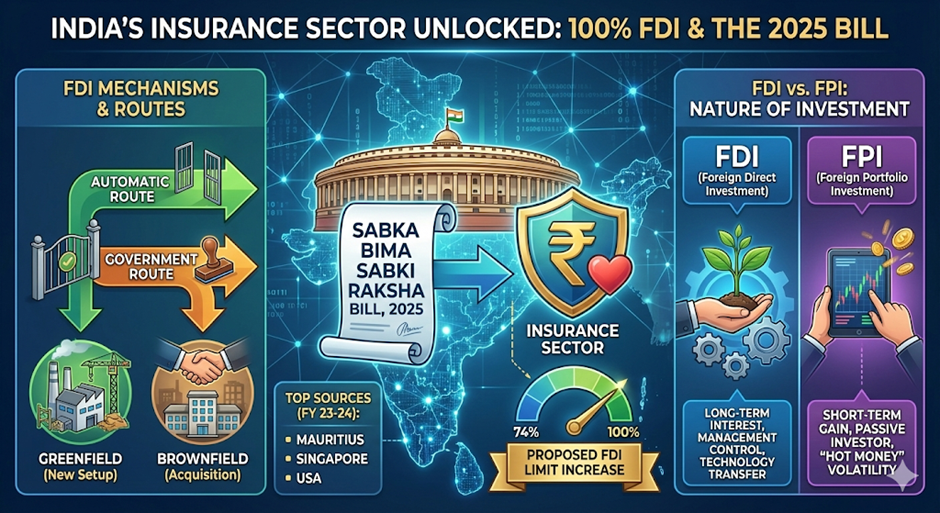
To align with the Budget FY26 announcements, the government has introduced the Sabka Bima Sabki Raksha (Amendment of Insurance Laws) Bill, 2025. The core objective is to raise the FDI cap in the insurance sector to accelerate growth and penetration.
1. Key Legislative Changes
- FDI Cap Increase: The Bill proposes increasing the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) limit in Indian insurance companies from 74% to 100%.
- Scope: This includes aggregate holdings by foreign investors, including Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs).
- Statutory Amendments: The Bill seeks to amend three parent acts:
- Insurance Act, 1938
- Life Insurance Corporation (LIC) Act, 1956
- IRDA Act, 1999
About FDI
1. Defining FDI
- Definition: Investment by a non-resident entity into a resident Indian company.
- The 10% Rule: An investment is classified as FDI if the stake acquired is 10% or more of the post-issue paid-up equity capital. (Less than 10% is typically treated as FPI).
- Nature: Involves long-term interest and management control.
2. Types of FDI
- Horizontal: Expanding the same business into a foreign country (e.g., McDonald’s opening in India).
- Vertical: Acquiring a business within the supply chain (e.g., A car maker acquiring a tyre manufacturer abroad).
- Conglomerate: Investing in an unrelated business (e.g., A tech firm investing in a clothing brand).
3. Modes of Entry
- Greenfield Investment: Setting up a new business from scratch (e.g., building a new factory).
- Brownfield Investment: Purchasing or merging with an existing facility/business.
4. Entry Routes in India
- Automatic Route: No prior government approval required (e.g., 100% in E-commerce marketplace).
- Government Route: Requires prior approval from the respective Ministry/Department.
India’s FDI Profile
Top Sources of FDI
- Mauritius (25%)
- Singapore (23%)
- USA (9%)
Top Sectors Attracting FDI
- Services Sector (Finance, Banking, Insurance) – 16%
- Computer Software & Hardware – 15%
- Trading – 6%
Sector-Specific Limits
| Sector | Limit | Route |
| Insurance (Proposed) | 100% | (Subject to conditions) |
| Space Sector | 100% | (Mix of Auto & Govt) |
| Defence | 74% | Automatic (100% via Govt) |
| Print Media | 26% | Automatic |
| Public Sector Banks | 20% | Government |
| Private Banks | 74% | (49% Auto + Govt beyond) |
Prohibited Sectors (The “Negative List”)
FDI is strictly banned in:
- Gambling, Betting, Casinos.
- Lottery Business (including private/government).
- Chit Funds & Nidhi Companies.
- Real Estate Business (except construction of townships/commercial projects) & Farmhouses.
- Manufacturing of Tobacco products (Cigars, Cigarettes).
- Atomic Energy & Railway Operations.
Comparative Analysis (FDI vs. FPI)
| Feature | Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) | Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) |
| Intent | Management Control & Long-term Interest. | Short-term Capital Gain (Financial Investment). |
| Role | Active Investor (participates in management). | Passive Investor (no management control). |
| Stability | Stable (hard to sell off assets quickly). | Volatile (“Hot Money” – easy to sell and exit). |
| Impact | Brings Technology, Capital, & Jobs. | Increases Market Liquidity & Capital depth. |
Q. With respect to the regulatory framework of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in India, consider the following statements:
1. Any equity investment by a non-resident entity which is less than 10% of the post-issue paid-up equity capital is classified as FDI.
2. The Consolidated FDI Policy is issued by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
3. 'Greenfield Investment' refers to Foreign Direct Investment involving the acquisition or merger with an existing facility in the host country.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is Incorrect: An investment is classified as FDI if it is 10% or more. Less than 10% is typically treated as Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI).
Statement 2 is Correct: The DPIIT (Ministry of Commerce) issues the Consolidated Policy, while FEMA is administered by the RBI.
Statement 3 is Incorrect: This definition describes Brownfield Investment. Greenfield refers to building a new operation from the ground up.