Why in the News?
- Recently, Mukalla gained international attention due to military and geopolitical developments involving the UAE-backed Southern Transitional Council (STC) and Saudi-led airstrikes targeting arms shipments.
- The city’s strategic location along the Gulf of Aden highlights its importance in maritime security, offshore energy logistics, and humanitarian operations.
Geographical Overview of Mukalla
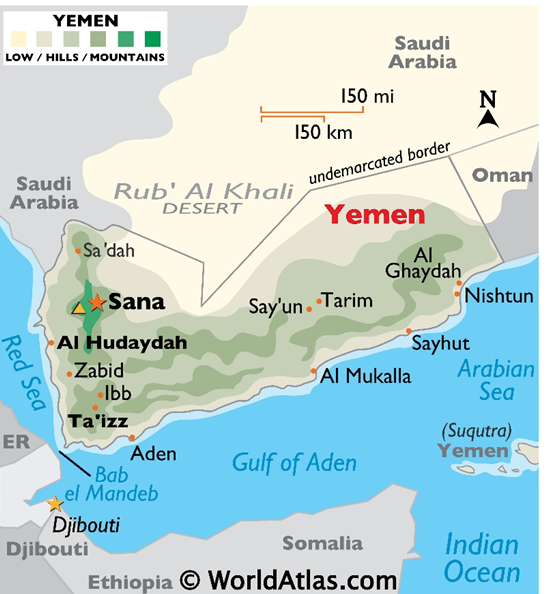
- Location: Mukalla is situated on the southern coast of Yemen, along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Aden, forming a strategic maritime corridor connecting the Red Sea to the Indian Ocean.
- Governorate: It serves as the capital of Hadhramaut Governorate, the largest governorate in Yemen.
Borders and Nearby Regions of Mukalla
- North: Hadhramaut highlands and interior Yemen.
- West: Shabwah Governorate (Yemen).
- East: Omani frontier and Arabian Sea coast.
- South: Directly faces the Arabian Sea; linked to the Gulf of Aden, a key shipping lane connecting to the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait.
Topography and Landforms of Mukalla
- Located on a narrow coastal plain backed by the Hadhramaut Mountains.
- Terrain transitions from low-lying plains to steep inland escarpments.
- Contains wadis (seasonal rivers) that drain into the Arabian Sea, forming small alluvial fans.
Oceans and Strategic Waterways of Mukalla
- Arabian Sea: Forms Mukalla’s coastal boundary, part of the northwestern Indian Ocean.
- Gulf of Aden: Lies south of Mukalla, forming a major shipping corridor linking the Red Sea (via Suez Canal) to the Arabian Sea and Indian Ocean.
Climate and Vegetation of Mukalla
- Climate: Hot desert climate (BWh) with high temperatures year-round and low annual rainfall.
- Vegetation: Sparse xerophytic shrubs; wadi beds support Acacia, Tamarix, and Mesquite trees adapted to arid conditions.
Economic Geography of Mukalla
- Port Activities: Fishing, trade, and handling of cement and oil.
- Air and Land Connectivity: Linked via Riyan International Airport and highways connecting inland Hadhramaut.
- Minerals and Natural Resources of Mukalla: Surrounding regions have limestone and gypsum deposits.No major mining activity occurs within Mukalla city itself.
Historical and Cultural Significance of Mukalla
- Known as the “Bride of the Arabian Sea” due to its coastal beauty and strategic importance.
- Historically, Mukalla served as a trading port connecting the Arabian Peninsula with East Africa and South Asia.
Strategic Significance of Mukalla
- Maritime Security: Mukalla’s location on the Gulf of Aden, near the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, makes it strategically crucial for India’s energy security, as approximately 30% of India’s crude oil imports pass through this maritime chokepoint.
- Stability in this region ensures uninterrupted access to global shipping lanes connecting the Indian Ocean with the Red Sea and Mediterranean Sea.
- Trade Protection: Mukalla lies along a major shipping corridor used by Indian merchant vessels, facilitating trade with East Africa, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Ensuring regional stability directly impacts the safety of India’s maritime commerce, minimizing risks from conflict or piracy.
- Counter-Piracy and Maritime Operations: The city’s proximity to the Gulf of Aden, a piracy-prone area, allows India to conduct anti-piracy patrols through the Indian Navy.
- Mukalla serves as a logistical reference point for naval operations aimed at protecting Indian ships and international trade from maritime terrorism.
- Geopolitical and Diplomatic Importance: Mukalla is controlled by the UAE-backed Southern Transitional Council (STC), and its instability impacts regional security dynamics involving Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Iran.
- India’s neutral diplomatic stance allows engagement in humanitarian aid while maintaining strategic ties in the region.
- Humanitarian and Emergency Operations: Mukalla’s strategic coastal location enables rapid evacuation of Indian nationals during crises.
- Historical precedent: Operation Rahat (2015), where Indian forces evacuated citizens from conflict zones in Yemen, relied on access through Mukalla and Aden.
- Energy and Offshore Logistics: Mukalla serves as a hub for offshore oil and gas transport, including personnel and material movement to nearby rigs and installations.
Q. Mukalla, recently in the news, is strategically important because:
1. Mukalla is located on the southern coast of Yemen, along the Arabian Sea.
2. The city lies near the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, a key chokepoint for global maritime trade.
3. Mukalla directly controls maritime traffic through the Strait of Hormuz.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Mukalla is a port city on Yemen’s southern coast, bordering the Arabian Sea.
Statement 2 is correct: Mukalla lies near the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, a vital maritime chokepoint connecting the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean, critical for global trade.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The Strait of Hormuz is located between Oman and Iran, far from Mukalla; Mukalla does not control traffic through it.