The World Health Organization (WHO) recently released its first global guidelines on the use of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) therapies for treating obesity in adults. While acknowledging the efficacy of these drugs, the WHO emphasized that medication must be part of a comprehensive strategy, not a standalone solution.
1. What is the Core Directive?
- Recommendation: GLP-1 therapies may be used for the long-term treatment of obesity in adults.
- Conditions:
- Exclusion: The guidelines specifically exclude pregnant women.
- Integrated Approach: Usage must be accompanied by intensive behavioural interventions, including dietary changes and physical activity.
- Status: The recommendation is “conditional” due to limited data on long-term safety, effects of discontinuation, and high costs affecting equitable access.
2. significance:
- Economic Impact: The global economic cost of obesity is projected to reach $3 trillion annually by 2030.
- Health Burden: Obesity is a key driver of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like cardiovascular disease, Type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Equity Concern: The guidelines highlight “equitable access” as a critical element, noting that high costs currently make these drugs inaccessible to many lower-income populations.
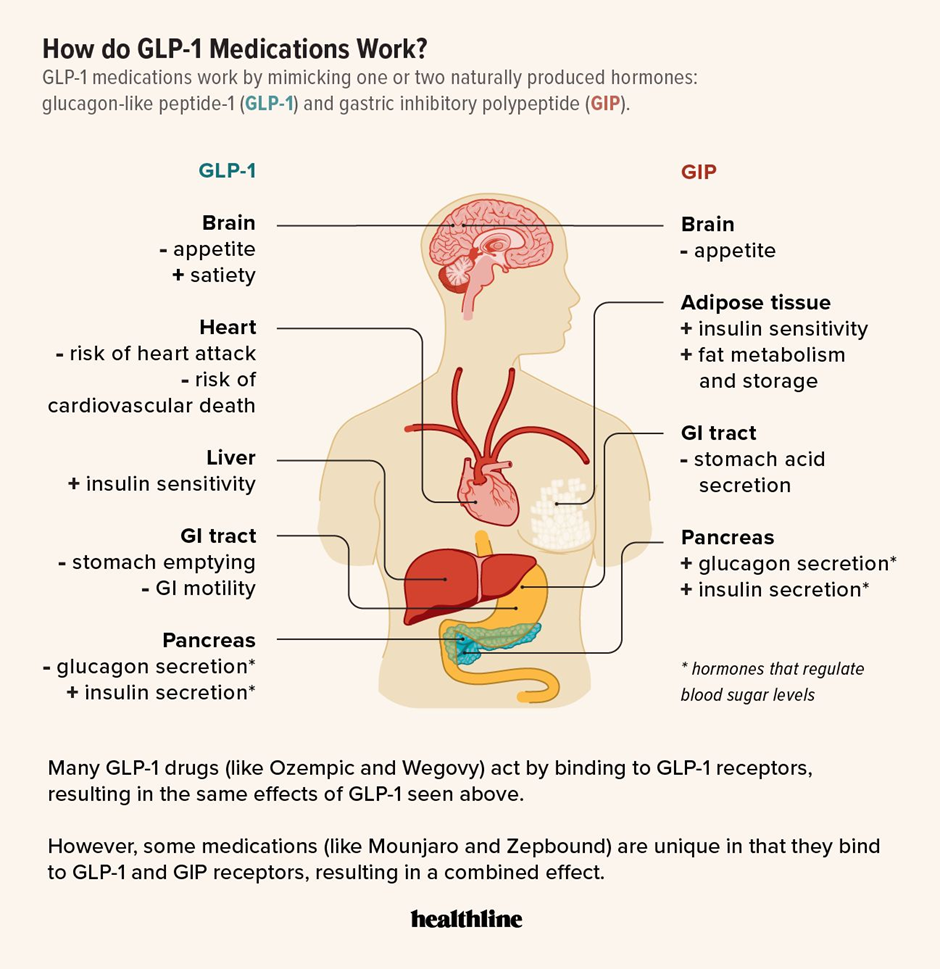
3. Science behind GLP-1:
- Biological Basis: GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is a natural incretin hormone released by the gut after food intake.
- Mechanism of Action:
- Insulin Regulation: Stimulates insulin secretion when glucose levels are high.
- Glucagon Inhibition: Reduces glucose output from the liver by inhibiting glucagon.
- Gastric Emptying: Slows down stomach emptying to prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Appetite Suppression: Signals satiety to the brain, reducing food intake.
- Drug Evolution: The hormone was isolated in 1986. Modern synthetic agonists (drugs) like Semaglutide (Novo Nordisk) and Tirzepatide (Eli Lilly) mimic this hormone but are more stable and effective.
4. How does this impact India?
- Availability: Major GLP-1 drugs (Semaglutide, Tirzepatide) have been introduced in the Indian market.
- Challenges: High cost remains a significant barrier for the general population.