Context
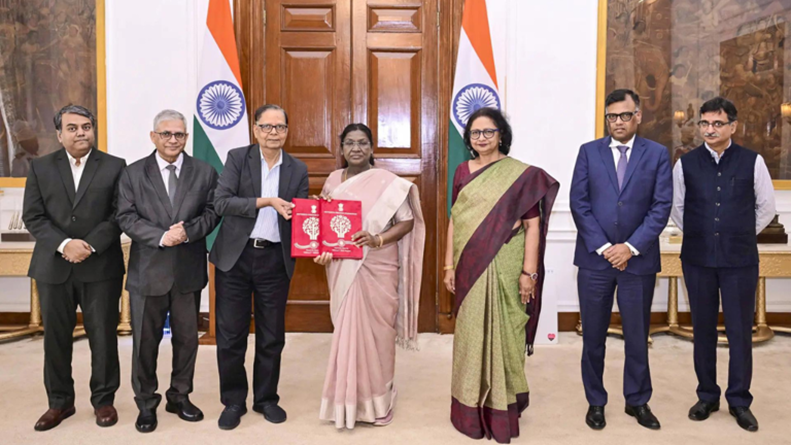
Recently, the Union Finance Minister tabled the report of the 16th Finance Commission in Parliament along with the Union Budget 2026-27. The government has accepted the Commission’s recommendation to maintain the vertical devolution of central taxes to States at 41% for the five-year period starting from April 1, 2026.
1. Constitutional and Statutory Framework
- Article 280: The Finance Commission (FC) is a quasi-judicial, constitutional body constituted by the President of India every five years or earlier.
- Article 281: It mandates the President to lay the recommendations of the FC, along with an Action Taken Memorandum (ATM), before both Houses of Parliament.
- Article 275: Deals with Grants-in-aid from the Consolidated Fund of India to specific states in need of assistance.
- Finance Commission Act, 1951: Provides the legal framework for the qualifications of the Chairman and members.
2. Qualifications for Members of the 16th FC
The Chairman
The Chairman must be a person having “experience in public affairs.” * This is a broad qualification, allowing for the appointment of eminent economists (like Dr. Arvind Panagariya), seasoned bureaucrats, or distinguished politicians.
The Four Members
The four members are selected from among people who possess the following specific qualifications:
- Judicial Expert: A person who is, or has been, or is qualified to be appointed as a Judge of a High Court.
- Financial Expert: A person who has specialized knowledge of the finances and accounts of the Government.
- Administrative Expert: A person who has had wide experience in financial matters and in administration.
- Economic Expert: A person who has specialized knowledge of economics.
3. Key Recommendations (2026-2031)
A. Vertical Devolution
- The Commission recommended retaining the share of states in the net proceeds of central taxes at 41%.
- The remaining 59% stays with the Centre to fund national priorities, defense, and centrally sponsored schemes.
B. Horizontal Devolution (The Distribution Formula)
The 16th FC adjusted the weights for distributing funds among states to balance “Equity” (need-based) and “Efficiency” (performance-based).
| Criterion | Weightage (16th FC) | Weightage (15th FC) |
| Income Distance | 42.5% | 45% |
| Population (2011 Census) | 17.5% | 15% |
| Area | 10% | 15% |
| Forest and Ecology | 10% | 10% |
| Demographic Performance | 10% | 12.5% |
| Contribution to GDP (New) | 10% | – |
| Tax & Fiscal Efforts | Removed | 2.5% |
C. Grants and Local Bodies
- Local Body Grants: Recommended ₹7.91 trillion for the award period, split 60:40 between rural and urban local bodies.
- Urbanization Premium: Introduced a ₹10,000 crore incentive to support states in transitioning from rural to urban governance.
- Wastewater Management: Allocated ₹56,100 crore specifically for revamping drainage systems in middle-level municipalities.
D. Fiscal Road Map
- State Deficits: Recommended capping states’ fiscal deficits at 3% of GSDP.
- Cesses and Surcharges: The Commission suggested a “grand bargain” where the Union folds a portion of cesses/surcharges into the divisible pool in exchange for state-level fiscal reforms.
In the context of the 16th Finance Commission’s horizontal devolution formula, consider the following criteria:
I. Income Distance
II. Population (2011)
III. Area
IV. Forest and Ecology
How many of the above are proposed to be used as criteria for horizontal devolution among States?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All the four
Correct Answer: (d) All the four
Solution
Statement I – CORRECT: Income Distance continues to remain the most important criterion under the 16th Finance Commission framework as well, since fiscal equalisation among States is a core constitutional mandate under Article 280.
Statement II – CORRECT: Population based on the 2011 Census is retained in the devolution formula to reflect current demographic realities rather than historical population figures.
Statement III – CORRECT: Area is included to compensate States that face higher administrative, infrastructure and service delivery costs due to large geographical size.
Statement IV – CORRECT: Forest and Ecology is included to reward States that preserve forest cover and ecological assets that provide national and global environmental benefits.