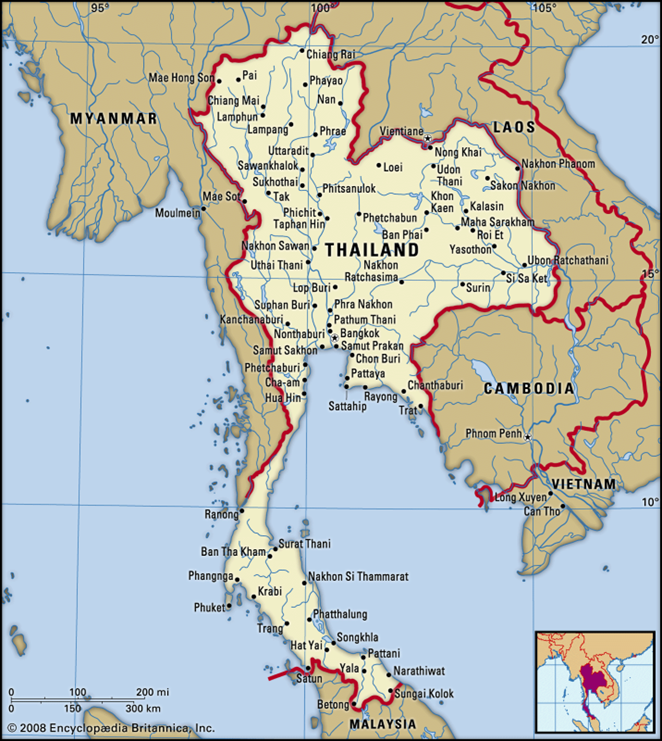
Geographic Positioning:-
- Region: Centrally located in mainland Southeast Asia.
- Land Borders:
- Maritime Boundaries: Flanked by the Andaman Sea to the west and the Gulf of Thailand to the east.
Physical Landscape:-
- Topography: The country features a diverse landscape ranging from mountainous highlands to river plains.
- Highest Peak: Doi Inthanon (located in the northern range).
- Major River Systems:
- Mekong River: Forms a natural border with Laos.
- Chao Phraya: The principal river system of the country, crucial for agriculture.
- Climatic Zone: Experiences a Tropical Monsoon climate.
Economic Resource Profile:-
- Natural Resources: Rich in Tin, Rubber, Natural Gas, Tungsten, Tantalum, and Timber.
Regional Spotlight: Sa kaeo Province
- Strategic Location: Situated in Eastern Thailand, sharing a critical land border with Cambodia.
- Trade Corridor: Hosts the Aranyaprathet-Poipet border crossing, the primary land route connecting Bangkok to Siem Reap (Angkor Wat).
- Cultural Heritage: Famous for Prasat Sdok Kok Thom, an 11th-century Khmer temple that historically clarified the chronology of the Khmer Empire.
- Connectivity: A vital node in the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) economic corridors.
Q. With respect to the physical geography and river systems of Thailand, consider the following statements:
1. The Mekong River forms a natural boundary between Thailand and Laos.
2. The Chao Phraya serves as the principal river system of the country.
3. The coastline is flanked by the Andaman Sea to the east and the Gulf of Thailand to the west.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The Mekong River forms the natural border to the northeast with Laos.
Statement 2 is correct: The Chao Phraya is the principal river system crucial for agriculture.
Statement 3 is incorrect: The Andaman Sea is to the west, and the Gulf of Thailand is to the east (the statement reverses these locations).