Why In News ?
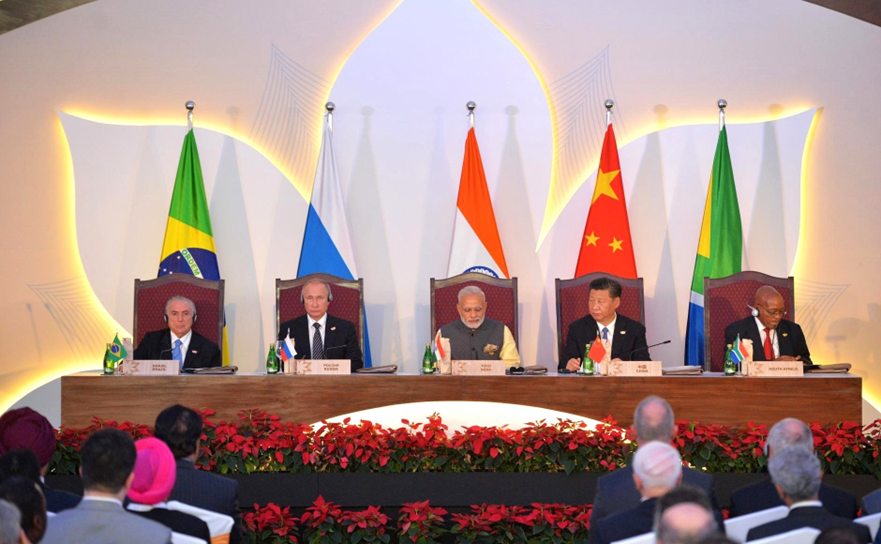
- Recently, Brazil formally handed over the BRICS Presidency to India for the year 2026, following the conclusion of the 17th BRICS Summit held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (July 2025).
- India is set to host the 18th BRICS Summit in 2026, focusing on the pillars of Resilience, Innovation, Cooperation, and Environmental Sustainability, furthermore, the group has seen significant consolidation after the inclusion of new members like Indonesia (joined 2025) and the earlier batch of Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, and the UAE.
1. Genesis and Evolution
- The Concept: The acronym BRIC was coined in 2001 by Jim O’Neill, a British economist at Goldman Sachs, to describe the four emerging economies (Brazil, Russia, India, and China) that were predicted to dominate the global economy by 2050.
- Formalization: The grouping began formal diplomatic engagement in 2006 during the UN General Assembly.
- First Summit: The 1st formal summit took place in Yekaterinburg, Russia, in 2009.
- Expansion to BRICS: South Africa was invited to join in December 2010 and attended its first summit in Sanya, China, in 2011, changing the name to BRICS.
- BRICS+ Expansion: In 2024-25, the bloc underwent its most significant expansion. Current members include:
- Original 5: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa.
- Expanded Members: Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Indonesia (latest full member).
- Note: Saudi Arabia has been invited but is yet to formalize; Argentina opted out in 2024.
2. Institutional Framework
The strength of BRICS lies in its financial institutions, which act as alternatives to the Bretton Woods twins (IMF and World Bank).
A. New Development Bank (NDB)
- Established: 2014 (6th BRICS Summit in Fortaleza, Brazil).
- Headquarters: Shanghai, China.
- Capital: Initial authorized capital of $100 billion.
- Voting: Unlike the World Bank, each founding member has equal voting power (one country, one vote) with no veto rights.
- Membership: Open to all UN members, but the share of BRICS founding members can never fall below 55%.
B. Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA)
- Purpose: To provide short-term liquidity support to members facing Balance of Payments (BoP) crises.
- Contribution: China ($41bn), India, Russia, Brazil ($18bn each), and South Africa ($5bn).
- Significance: Reduces dependence on the IMF during financial volatility.
3. Key Pillars of Cooperation
BRICS cooperation is structured around three main pillars:
- Political and Security: Reforming global governance (UNSC, WTO) and counter-terrorism.
- Economic and Financial: Trade, NDB projects, and the BRICS Payment System (alternative to SWIFT).
- Cultural and People-to-People: BRICS Games, Youth Summit, and Academic Forum.
4. Recent Summit Highlights (17th Summit – Rio 2025)
- Theme: “Strengthening Global South Cooperation for More Inclusive and Sustainable Governance.”
- Rio de Janeiro Declaration: Focused on reforming the UN Security Council to include more representation from Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
- New Initiatives: Launch of the BRICS Space Council and the Leaders’ Statement on Global AI Governance.
- Climate Finance: Adopted a framework to mobilize resources for developing nations without protectionist trade barriers.
Q. Consider the following statements regarding the BRICS grouping:
I. The New Development Bank (NDB) operates on a weighted voting system where the vote share is proportional to the capital contribution of the member country.
II. The 18th BRICS Summit in 2026 is scheduled to be held in India.
III. Indonesia is the most recent nation to officially join as a full member of the BRICS+ framework.
IV. The Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) was established through the Fortaleza Declaration.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I, II and III only
(b) II, III and IV only
(c) I and IV only
(d) I, II, III and IV
Correct Answer: (b)
Solution
Statement I Incorrect: Unlike the IMF/World Bank, the NDB provides equal voting rights to its founding members; no member has veto power.
Statement II Correct: Following the 2025 Brazil summit, the rotating presidency was handed over to India for 2026.
Statement III Correct: Indonesia officially joined as a full member in 2025, expanding the bloc beyond the 2024 entrants.
Statement IV Correct: Both the NDB and the CRA were officially established during the 6th BRICS Summit in Fortaleza, Brazil (2014).