Why In the News?
- Recently, Yemen experienced significant political and security realignments as the Saudi-backed Presidential Leadership Council (PLC) launched a counter-offensive to recapture the oil-rich provinces of Hadramawt and Al-Mahra from the UAE-backed Southern Transitional Council (STC) following a month-long conflict.
- This development compelled the STC leadership to exit the country, followed by the formal dissolution of the organisation. Simultaneously, the United Nations has cautioned that Yemen’s humanitarian situation is expected to worsen, due to acute funding constraints and the lapse of maritime reporting mechanisms.
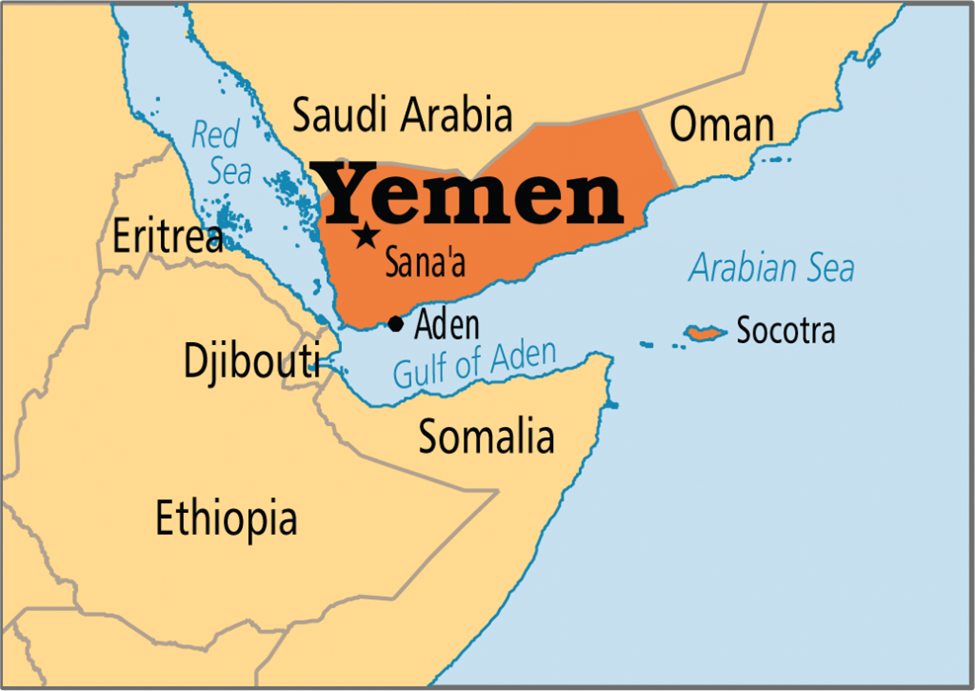
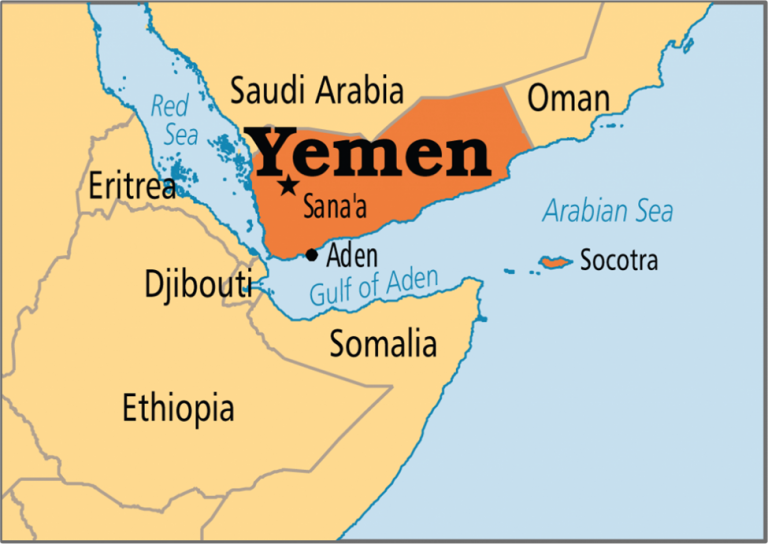
1. Geographical Profile: Yemen
For the UPSC Prelims, mapping is the most critical aspect of Yemen.
- Location: Situated at the southwestern tip of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia.
- Land Borders:
- North: Saudi Arabia
- East: Oman
- Water Bodies:
- West: Red Sea
- South: Gulf of Aden
- Southeast: Arabian Sea
- Strategic Chokepoints:
- Bab-el-Mandeb Strait: Connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden. It is often referred to as “Gate of Tears.”
- Strategic Islands:
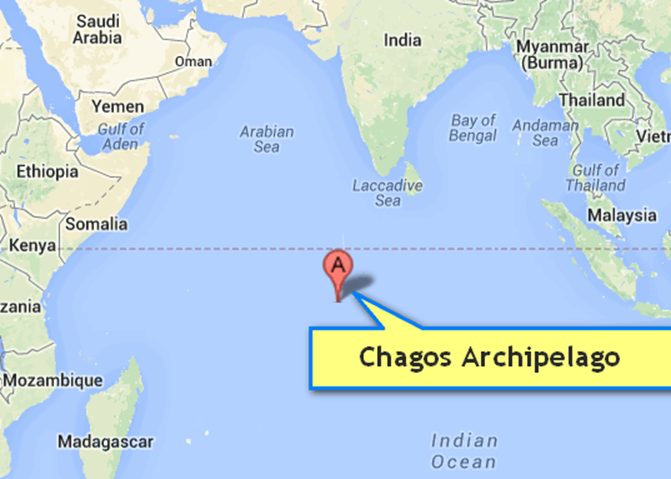
- Socotra Archipelago: Located in the Indian Ocean, it is a UNESCO World Heritage site known for its unique flora like the Dragon Blood Tree.
- Perim Island (Mayun): A volcanic island in the Bab-el-Mandeb strait that provides control over the shipping lane.
2. The Internal Crisis: PLC vs. STC vs. Houthis
- The Houthi Movement: An Iran-aligned group (Zaydi Shia) that controls the capital, Sana’a, and much of Northern Yemen. They continue to pose a threat to Red Sea shipping.
- Presidential Leadership Council (PLC): The internationally recognized government of Yemen, primarily supported by Saudi Arabia.
- Southern Transitional Council (STC) Collapse: Formerly an ally of the PLC against the Houthis, the STC sought an independent South Yemen. In early 2026, their attempt to seize eastern oil fields led to their expulsion from the government and subsequent dissolution.
- The Saudi-UAE Rift: The 2026 conflict highlighted a diverging strategy between Saudi Arabia (favoring a unified Yemen) and the UAE (which had historically supported southern secessionists).
3. Red Sea Security and Global Trade
- UN Resolution 2812 (2026): Adopted in January 2026, it extends the monthly reporting requirement on Houthi attacks in the Red Sea until July 15, 2026.
- Shipping Status: While major carriers like Maersk and CMA CGM have begun a gradual return to the Suez Canal route in early 2026, the security environment remains “volatile” with new Houthi threats emerging toward “Zionist positions” in the Horn of Africa (Somaliland).
- Maritime Impact: In late 2025, container traffic through the Suez Canal was nearly 45% lower than 2024 levels, leading to increased global freight costs.
4. India’s Strategic Interests
- Energy Security: Yemen’s proximity to the Bab-el-Mandeb makes it vital for India’s oil imports coming from the Atlantic and Mediterranean regions.
- Operation Raahat: India’s landmark 2015 evacuation mission remains a case study for Indian diplomacy and military coordination.
- Maritime Security: The Indian Navy maintains a persistent presence in the Gulf of Aden to provide “naval protection” to Indian-flagged merchant vessels against piracy and missile threats.
Q. Consider the following statements regarding the current situation and geography of Yemen:
1. Yemen is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the North, Oman to the East, and the United Arab Emirates to the Northeast.
2. The Bab-el-Mandeb Strait is a strategic chokepoint that connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
3. The Southern Transitional Council (STC) is a Houthi-aligned group that recently dissolved itself in January 2026.
4. UN Security Council Resolution 2812, adopted in 2026, focuses on monitoring attacks on commercial vessels in the Red Sea.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A) 1, 2, and 4 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2, 3, and 4 only
Correct Answer: (B)
Solution
STATEMENT 1 INCORRECT: Yemen shares land borders with Saudi Arabia and Oman. It does not share a land border with the United Arab Emirates.
STATEMENT 2 CORRECT: This is the primary geographical feature of the region; the Bab-el-Mandeb connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
STATEMENT 3 INCORRECT: The STC was a separatist group in the south, often allied with the government (PLC) against the Houthis. It was not Houthi aligned.
STATEMENT 4 CORRECT: Resolution 2812 (2026) was recently passed to extend the monitoring of Houthi maritime attacks