After Reading This Article You Can Solve This UPSC Mains Model Question:
The Union Budget 2026–27 reflects a calibrated approach towards growth, inclusion, and fiscal consolidation.” Critically examine this statement in the context of India’s goal of achieving Viksit Bharat 2047. 250 words (GS-3, Economy).
CONTEXT
The Union Budget 2026–27, presented by Nirmala Sitharaman, is the first Budget prepared in Kartavya Bhawan, symbolising a shift from entitlement-based governance to duty-driven (“Kartavya”) development.
It is framed around three Kartavyas, aiming to balance growth, inclusion, and resilience amid global economic volatility, supply-chain realignments, and India’s aspiration of Viksit Bharat @2047.
Macroeconomic Snapshot
- Total Expenditure (BE 2026–27): ₹53.5 lakh crore
- Non-debt Receipts: ₹36.5 lakh crore
- Net Tax Receipts: ₹28.7 lakh crore
- Capital Expenditure: ~₹12.2 lakh crore (growth-oriented stance)
- Fiscal Deficit: 4.3% of GDP (glide path consolidation)
- Debt–GDP Ratio: 55.6% (improving sustainability)
Philosophy & Framework of the Budget
The Budget is anchored in three Kartavyas, reflecting a transition from entitlement-based to responsibility-based public policy.
1️. First Kartavya – Accelerate & Sustain Economic Growth
- Enhance productivity and competitiveness
- Build resilience against volatile global economic conditions
2. Second Kartavya – Fulfil Aspirations & Build Human Capacity
- Empower citizens as partners in India’s growth
- Focus on skills, employability, and services-led growth
3. Third Kartavya – Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas
- Ensure equitable access to resources and opportunities
- Focus on regions, communities, and vulnerable sections
1. FIRST KARTAVYA: ACCELERATE & SUSTAIN ECONOMIC GROWTH
I. Manufacturing Push in Strategic & Frontier Sectors
(a) Biopharma SHAKTI (Strategy for Healthcare Advancement through Knowledge, Technology and Innovation)
- ₹10,000 crore (5 years) to position India as a global biopharma hub
- New & upgraded National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER), 1,000+ clinical trial sites
Significance: Moves India up the pharma value chain
(b) India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) 2.0
- Focus on equipment, materials, full-stack IP, and industry-led R&D
- Reduces import dependence, strengthens strategic autonomy
(c) Electronics Components Manufacturing
- Outlay enhanced to ₹40,000 crore
- Complements PLI ecosystem
(d) Rare Earth Corridors
- Odisha, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu
(e) Chemical Parks & Capital Goods
- 3 Chemical Parks (challenge mode)
- Hi-Tech Tool Rooms, CIE Scheme, Container Manufacturing (₹10,000 crore)
II. Integrated Programme for Textile Sector
- National Fibre Scheme:
Natural fibres (silk, wool, jute), man-made & new-age fibres - Textile Expansion & Employment Scheme:
Cluster modernisation, machinery, testing & certification - Mega Textile Parks:
Focus on technical textiles, value addition - Mahatma Gandhi Gram Swaraj Initiative:
Khadi, handloom & handicrafts + branding & global linkage
III. Rejuvenation of Legacy Industrial Clusters
- 200 clusters to be revived via infrastructure & technology upgrade
IV. Champion SMEs & Micro Enterprises
- ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund to create future Champions, incentivizing enterprises based onselect criteria
- Additional ₹2,000 crore to Self-Reliant India Fund to continue support to micro enterprises and maintain their access to risk capital.
- Corporate Mitras via ICAI/ICSI/ICMAI to design short-term, modular courses and practical tools.
V. Infrastructure as Growth Engine
- Public Capex: ₹12.2 lakh crore
- Infrastructure Risk Guarantee Fund (crowding-in private investment)
- New Dedicated Freight Corridor (Dankuni–Surat)
- 20 National Waterways (5 years)
- Start: NW-5 (Odisha – Talcher/Angul to Paradeep/Dhamra)
- Ship repair hubs: Varanasi & Patna
- Coastal Cargo Promotion Scheme- Modal share: 6% → 12% by 2047
- Seaplane VGF Scheme (connectivity + tourism)
VI. Energy Security & Climate Action
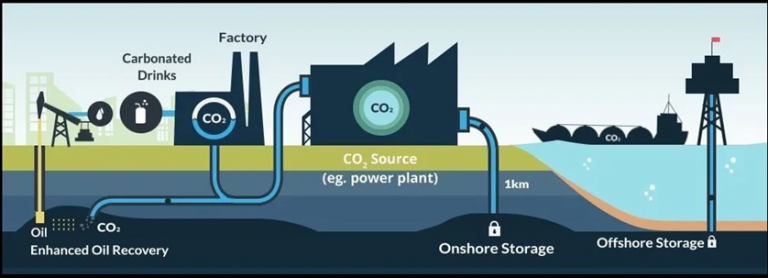
- ₹20,000 crore for Carbon Capture Utilisation & Storage (CCUS)
VII. City Economic Regions (CERs)
- ₹5,000 crore per CER (5 years)
- 7 High-Speed Rail Corridors as growth connectors
- Municipal Bonds: ₹100 crore incentive for issuances >₹1000 crore
2. SECOND KARTAVYA: ASPIRATIONS & HUMAN CAPITAL
I. Services-Led Growth
- High-Powered Education-to-Employment & Enterprise Committee recommends measures that focus on the ServicesSector as a core driver of Viksit Bharat.
II. Health & Human Resources
- 100,000 Allied Health Professionals to be added over the next 5 years.
- 5 Regional Medical Hubs (medical tourism)
- 3 new All India Institutes of Ayurveda
- 1 girls’ hostel to be established in every district
III. Orange Economy (AVGC)
- Visual Effects, Gaming and Comics (AVGC) labs in 15,000 schools & 500 colleges, Support via Indian Institute of Creative Technologies, Mumbai
IV. Tourism, Culture & Sports
- National Institute of Hospitality
- 10,000 trained tourist guides in 20 tourist sites
- National Destination Digital Knowledge Grid to digitally document all places of significance—cultural, spiritual andheritage.
- 15 iconic heritage sites (Lothal, Dholavira, Rakhigarhi, Adichanallur, Sarnath, Hastinapur, and Leh Palace etc.) to be developed into vibrant, experiential cultural destinations
- Khelo India Mission (decade-long vision)
3. THIRD KARTAVYA: SABKA SATH, SABKA VIKAS
I. Increasing Farmer Incomes (Centred on water security, crop diversification, and digital enablement).
- Integrated development of 500 reservoirs & Amrit Sarovars to reinforce irrigation capacity, ensure reliable water availability, and strengthen rural livelihoods.
- High-value crops: coconut, sandalwood, cocoa, cashew
- Coconut Promotion Scheme
- Bharat-VISTAAR: (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources)— a multilingual, AI-enabled platform that integrates AgriStack portals with ICAR’s agricultural practice packages,
II. Empowering Divyangjan
- Divyangjan Kaushal Yojana (IT, AVGC, hospitality)
III. Mental Health & Trauma Care
- NIMHANS-2 in North India
- Upgrade Ranchi & Tezpur institutes as regional apex bodies.
IV. Purvodaya & North-East Focus
- East Coast Industrial Corridor (node at Durgapur)
- 5 tourism destinations in Purvodaya States
- 4,000 e-buses
- Development of Buddhist Circuits in Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Assam, Manipur, Mizoram and Tripura.
Fiscal Federalism: Government provided ₹1.4 lakh crore to the States for the FY 2026-27 as Finance Commission Grants as recommended by the 16th Finance Commission.
Critical Analysis of Union Budget 2026–27
Strengths of Union Budget 2026–27
- Strong growth push with fiscal prudence: Public capital expenditure raised to ₹12.2 lakh crore, while fiscal deficit reduced to 4.3% of GDP (from 4.4% in 2025–26).
- Manufacturing and self-reliance focus: Major allocations such as ₹40,000 crore for electronics components, ₹10,000 crore for Biopharma SHAKTI, and ₹10,000+ crore for container manufacturing strengthen industrial depth.
- Infrastructure-led multiplier effect: Total expenditure at ₹53.5 lakh crore, with large investments in freight corridors, waterways (20 NWs), and high-speed rail to boost logistics efficiency.
- Support to MSMEs and entrepreneurship: ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund and ₹2,000 crore additional support to the Self-Reliant India Fund improve access to risk capital.
- Energy and sustainability orientation: ₹20,000 crore committed over five years for Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS), aligning growth with climate goals.
- Human capital and services emphasis: Creation of 100,000 Allied Health Professionals, AVGC labs in 15,000 schools and 500 colleges, and tourism skill initiatives strengthen employment potential.
- Balanced regional and social inclusion: Targeted spending on Purvodaya & North-East, agriculture (500 reservoirs, Amrit Sarovars), and ₹1.4 lakh crore Finance Commission grants to States.
Concerns of Union Budget 2026–27
- High borrowing requirement: Gross market borrowing at ₹17.2 lakh crore keeps pressure on interest rates and private investment (crowding-out risk).
- Revenue dependence on optimistic assumptions: Net tax receipts projected at ₹28.7 lakh crore may be vulnerable to global slowdown and trade uncertainties.
- Implementation capacity risks: Large-scale initiatives—200 legacy clusters, 20 national waterways, 7 high-speed rail corridors—demand strong Centre–State coordination.
- Limited direct income support to farmers: Despite structural measures (500 reservoirs, high-value crops), absence of major enhancement in direct income transfers may delay short-term relief.
- Private investment uncertainty: Infrastructure Risk Guarantee Fund announced, but effectiveness depends on design; private capex response remains unclear.
- Social sector outlay visibility: While programmes are announced (mental health, Divyangjan, skills), explicit budgetary allocations for some schemes are not clearly specified.
WAY FORWARD
- Strengthen implementation: Ensure time-bound execution through robust Centre–State coordination, outcome-based monitoring, and third-party audits.
- Deepen fiscal consolidation: Gradually reduce debt–GDP ratio by broadening the tax base, improving compliance, and rationalising non-merit subsidies.
- Crowd-in private investment: Operationalise the Infrastructure Risk Guarantee Fund with clear rules to unlock private and foreign capital.
- Boost farm incomes faster: Complement structural reforms with targeted income and price-risk support, stronger agri-value chains, and export facilitation.
- Enhance human capital delivery: Align skilling, education, and health initiatives with industry demand through PPPs and district-level skill mapping.
- Improve transparency: Clearly earmark and disclose scheme-wise allocations and outcomes to strengthen credibility and accountability.
CONCLUSION
The Union Budget 2026–27 lays the foundation for Viksit Bharat 2047 by combining fiscal discipline, manufacturing-led growth, and human capital investment. Its focus on infrastructure, technology-driven agriculture, green transition, and inclusive regional development positions India to transform demographic potential into sustainable, globally competitive prosperity.