Context
Recently, the Ministry of Steel has taken a pioneering step by releasing the “Green Steel Taxonomy,” making India the first country globally to establish a formal carbon footprint standard for steel production.
This development aligns with the “Green Steel Mission,” a ₹15,000-crore initiative designed to decarbonize the Indian steel industry and support the national goal of achieving Net-Zero emissions by 2070.
1. What is Green Steel?
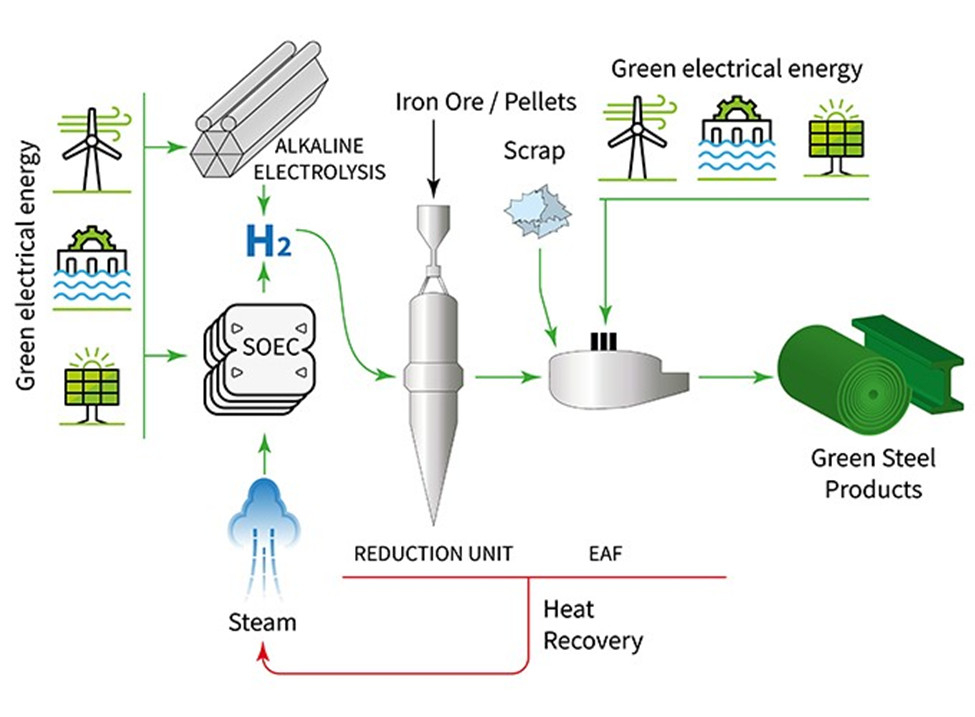
- Definition: Green Steel refers to the manufacturing of steel without the use of fossil fuels, utilizing low-carbon energy sources like Green Hydrogen, renewable electricity, or biomass.
- India’s Threshold: According to the Ministry of Steel, steel is categorized as “Green” only if its carbon dioxide equivalent emission intensity is less than 2.2 tonnes of CO2 per tonne of finished steel.
- Current Scenario: The average emission intensity for the Indian steel industry currently stands at approximately 2.5–2.6 tonnes of CO2 per tonne of finished steel.
2. Production Methods
- Green Hydrogen-Based DRI: Replaces coking coal with green hydrogen as a reducing agent in the Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) process.
- Electric Arc Furnace (EAF): Uses renewable electricity to melt steel scrap or DRI, significantly reducing the reliance on traditional Blast Furnaces.
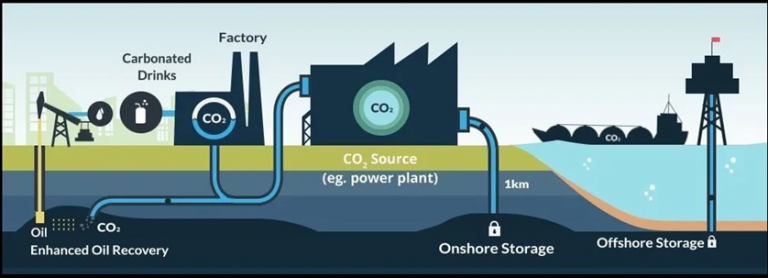
- Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS): Captures emissions from conventional plants to prevent them from entering the atmosphere.
- Steel Scrap Recycling: Utilizing ferrous scrap reduces the energy required for smelting compared to primary ore processing.
3. Key Government Initiatives
- Green Steel Mission: A comprehensive roadmap with a budget of ₹15,000 crore focusing on technology switchover and public procurement mandates (up to 37% for 5-star green steel).
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: Has allocated ₹455 crore for pilot projects specifically in the steel sector.
- Steel Scrap Recycling Policy (2019): Aims to increase the availability of domestically generated scrap to reduce coal consumption.
- Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) Scheme: A market-based mechanism under the National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE) that incentivizes energy savings in the steel sector.
- Green Steel Taxonomy: Provides the standards for measurement, reporting, and verification (MRV) handled by the National Institute of Secondary Steel Technology (NISST).
4. Facts about Steel Sector in India
- India is currently the world’s 2nd largest producer of crude steel and the largest producer of Direct Reduced Iron (DRI)/Sponge Iron.
- The steel industry is a “Hard-to-Abate” sector, contributing roughly 7-8% of global CO2 emissions and a significant portion of India’s industrial emissions.
- Major pollutants from traditional steel plants include Oxides of Sulphur, Oxides of Nitrogen (Nox), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Particulate Matter (PM 2.5).
Q. With reference to 'Green Steel' in India, consider the following statements:
1. Under the newly released Green Steel Taxonomy, any steel with an emission intensity exceeding 2.2 tonnes of CO2 equivalent per tonne of finished steel is not considered green steel.
2. The National Institute of Secondary Steel Technology (NISST) is the nodal agency for issuing greenness certificates and star ratings for steel plants.
3. India is the first country in the world to formally define a taxonomy for green steel.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Solution: (c)
STATEMENT 1 CORRECT: The Ministry of Steel has set the threshold for green steel at less than 2.2 tonnes of CO2 equivalent per tonne of finished steel, anything above this does not qualify for a star rating.
STATEMENT 2 CORRECT: NISST is responsible for the Measurement, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) process and issuing the star ratings annually.
STATEMENT 3 CORRECT: India has indeed become the first country globally to define a specific taxonomy and star-rating system for green steel to facilitate its market and transition