Context
Recently, India and the six-nation Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) officially signed the Terms of Reference (ToR) to launch formal negotiations for a long-pending Free Trade Agreement (FTA). This significant diplomatic step, announced during a high-level meeting in New Delhi, aims to revitalize trade talks that have been stalled for nearly two decades.
The move is particularly timely as the GCC has emerged as India’s largest merchandise trading partner, with bilateral trade reaching approximately $178.5 billion in the 2024-25 fiscal year.
1. About the GCC
- Establishment: The GCC is a political and economic alliance of six Middle Eastern nations established on May 25, 1981, in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
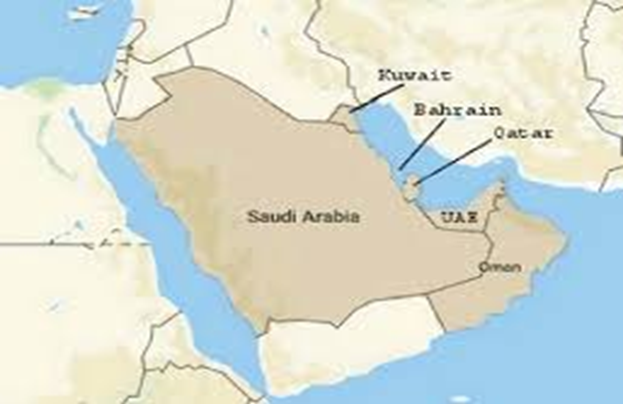
- Member States: It comprises United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, Kuwait, and Bahrain.
- Headquarters: The Secretariat-General is located in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
- Objectives: Its primary goal is to achieve coordination, integration, and interconnection between its members in all fields, including economy, finance, trade, and customs.
- Structure:
- Supreme Council: The highest authority, composed of the Heads of State; the presidency rotates annually.
- Ministerial Council: Composed of Foreign Ministers who meet every three months to implement policies.
- Secretariat General: The administrative arm responsible for policy monitoring.
2. India-GCC Economic Relations
- Largest Trade Partner: The GCC as a bloc is India’s largest trading partner. In 2024-25, trade with the GCC surpassed that with the USA ($132.1 billion) and the European Union ($136.5 billion).
- Trade Deficit: India currently faces a significant trade deficit with the region (approx. $64.8 billion) due to heavy imports of crude oil, LNG, and petrochemicals.
- Key Exports: India primarily exports engineering goods, rice, textiles, machinery, and gems and jewelry to the Gulf nations.
- Remittances: The region is home to nearly 10 million Indian expatriates, who contribute significantly to India’s foreign exchange through remittances.
3. Energy and Strategic Security
- Energy Anchor: The GCC countries contribute significantly to India’s energy security, accounting for roughly 35% of oil imports and 70% of gas imports.
- Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR): India is engaging GCC nations like Saudi Arabia and the UAE to participate in the second phase of its SPR program.
- Strategic Partnerships: While India maintains close ties with all six members, it has formal “Strategic Partnership” agreements with Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Oman.
4. Recent Initiatives
- FTA Negotiations (2026): The signing of the Terms of Reference (ToR) in February 2026 sets the framework for scope, objectives, and procedures for the final trade pact.
- Unified Tourist Visa: The GCC is working toward a “Schengen-style” unified tourist visa (expected pilot in late 2026) to allow seamless travel across all six member states.
Q. With reference to the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), consider the following statements:
1. It is a regional intergovernmental union comprising all the littoral states of the Persian Gulf.
2. The Supreme Council is the highest authority of the GCC, and its presidency rotates periodically among the Member States.
3. As of 2025, the GCC as a bloc has surpassed the United States and the European Union to become India's largest merchandise trading partner.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
A) Only one
B) Only two
C) All three
D) None
Correct Answer: B (Only two)
Explanation
STATEMENT 1 IS INCORRECT: While the GCC countries are located around the Persian Gulf, the council does not include all littoral states. Specifically, Iran and Iraq are littoral states of the Persian Gulf but are not members of the GCC.
STATEMENT 2 IS CORRECT: The Supreme Council, consisting of the Heads of State, is the top decision-making body, and its presidency rotates among members in alphabetical order.
STATEMENT 3 IS CORRECT: According to the latest trade data (2024-25), India’s total bilateral merchandise trade with the GCC stood at $178.5 billion, which is higher than its trade with the EU ($136.5 billion) and the US ($132.1 billion).