Context
Recently, Sudan has witnessed a major strategic shift in its ongoing civil war between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF). The Sudanese military recently claimed to have regained control over significant portions of the capital, Khartoum, and the strategic city of Wad Medani, signaling a potential turning point in the conflict.
Concurrently, the international community has raised alarms over the humanitarian blockade in El Fasher, the last major stronghold in the Darfur region not fully controlled by paramilitary forces, making the geographical understanding of these urban centers vital for global security analysis.
1. Geographical Location and Borders
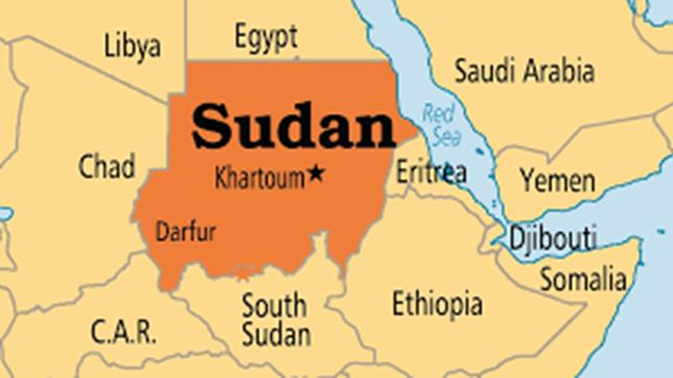
Sudan is located in Northeast Africa and is the third-largest country on the African continent (after Algeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo). It is not landlocked; it possesses a strategic coastline of approximately 853 km along the Red Sea.
Neighboring Countries (Clockwise from North):
- Egypt (North)
- Eritrea (Southeast)
- Ethiopia (Southeast)
- South Sudan (South) — Seceded in 2011
- Central African Republic (Southwest)
- Chad (West)
- Libya (Northwest)
2. Key Physical Features
- The Nile River System: The White Nile (flowing from Lake Victoria) and the Blue Nile (flowing from Lake Tana, Ethiopia) meet in the heart of Khartoum to form the main Nile River, which then flows north into Egypt.
- Red Sea Hills: A range of mountains running parallel to the Red Sea in the east.
- Marrah Mountains (Jebel Marra): Located in the Darfur region of the west, containing the Deriba Caldera, the highest point in Sudan.
- Nubian Desert: Covers the northeastern part of the country, situated between the Nile and the Red Sea.
- Gezira Plain: The fertile “peninsula” between the Blue and White Niles, south of Khartoum, known for the Gezira Scheme (one of the world’s largest irrigation projects).
3. Important Cities and Their Strategic Significance
| City | Significance |
| Khartoum | The capital city located at the confluence (Al-Mugran) of the Blue and White Niles. |
| Omdurman | Located on the west bank of the Nile, it is the country’s most populous city and a major cultural hub. |
| Port Sudan | The primary seaport on the Red Sea. It has become the de-facto administrative capital during the current conflict. |
| El Fasher | The capital of North Darfur; a critical humanitarian hub and a major site of ongoing battles. |
| Wad Medani | Capital of the Gezira state; a strategic agricultural and transit hub between Khartoum and Port Sudan. |
| Wadi Halfa | A key border town in the north near Lake Nubia, serving as a primary transit point for trade with Egypt. |
Q. Consider the following pairs of places in Sudan and the reasons they were recently in the news:
Place Context / Significance
1. El Fasher Last SAF stronghold in the Darfur region
2. Port Sudan Main maritime outlet for Sudanese oil and exports
3. Khartoum Confluence of the White Nile and Blue Nile
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
A) Only one
B) Only two
C) All three
D) None
Answer: C) All three
Solution:
STATEMENT 1 CORRECT: El Fasher is the capital of North Darfur and has been the focus of international concern as the last major city in the region held by the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) amidst RSF advances.
STATEMENT 2 CORRECT: Port Sudan is the nation's principal port on the Red Sea and serves as the primary gateway for international trade and humanitarian aid.
STATEMENT 3 CORRECT: Khartoum is geographically famous for being the site where the White Nile and the Blue Nile merge to form the Nile River.